
Science in Space March 2025
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is regularly used on the ground to quickly produce a variety of devices. Adapting this process for space could let crew members create tools and parts for maintenance and repair of equipment on the spot, rather than trying to bring along every item that might be needed.
The ability to manufacture things in space is especially important in planning for missions to the Moon and Mars because additional supplies cannot quickly be sent from Earth and cargo capacity is limited.
Research on the International Space Station is helping to develop the capability to address multiple needs using 3D printing.
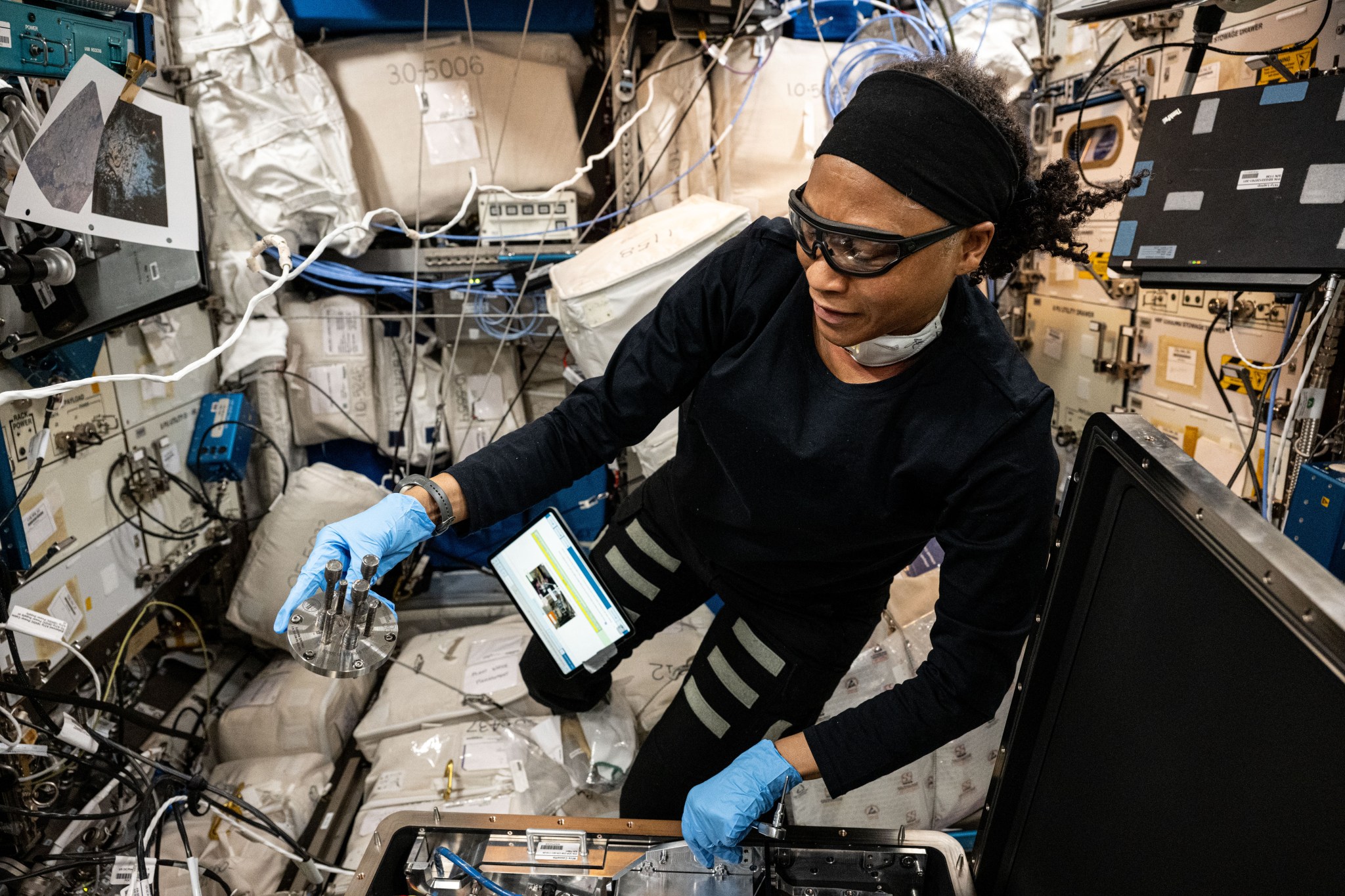

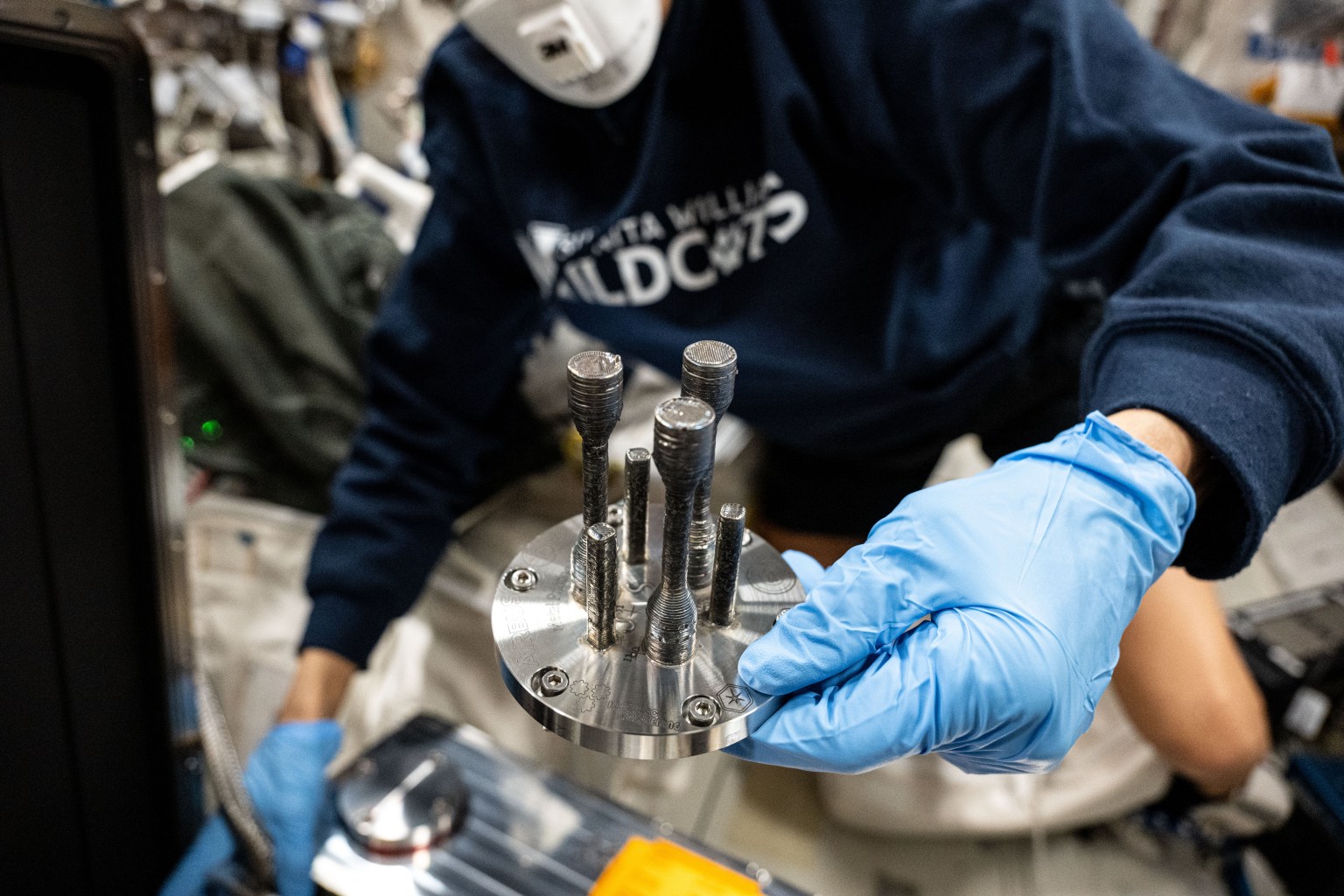
Metal 3D Printer, a current investigation from ESA (European Space Agency), tests 3D printing of small metal parts in microgravity. Results could improve understanding of the function, performance, and operations of 3D printing in space with metal, as well as the quality, strength, and characteristics of printed parts. This work also could benefit applications on Earth that use metal, such as the automotive, aeronautical, and maritime industries.
Printing with plastic
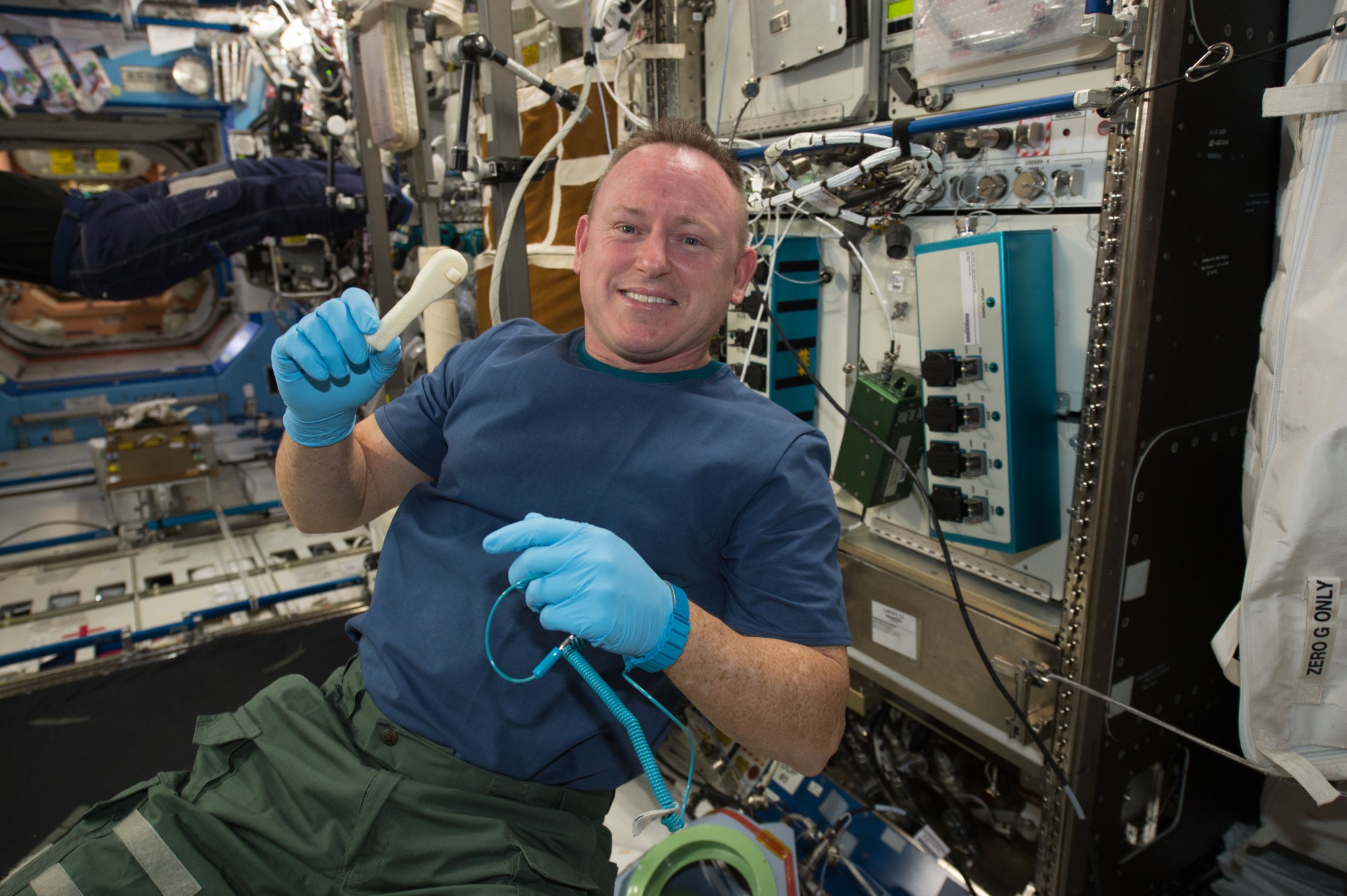

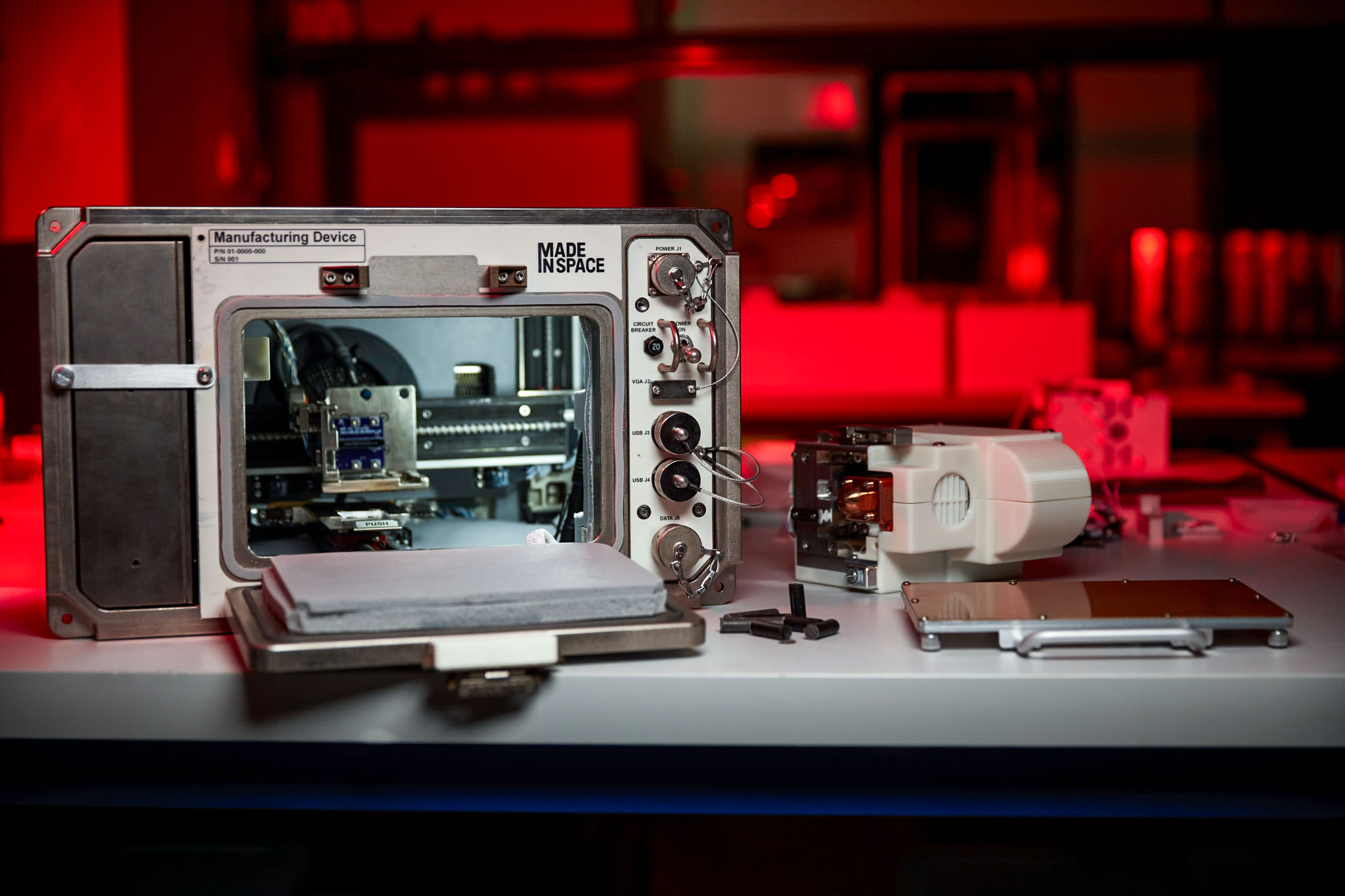
3D Printing in Zero-G sent the first 3D printer, developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and Redwire (formerly Made in Space), to the space station in 2014. The printer used a process that feeds a continuous thread of plastic through a heated extruder and onto a tray layer by layer to create an object. The investigation produced more than a dozen parts, including a ratchet wrench, showing that researchers could send a design from the ground to the system on the station more than 200 miles above.
Comparing the parts made in space with those made on the ground showed that microgravity had no significant effect on the process.
Redwire then developed the Additive Manufacturing Facility (AMF), sent to the station in 2015. Researchers evaluated its mechanical performance and found improvements in tension strength and flexibility compared to the earlier demonstration, helping to further the technology for this type of manufacturing on Earth and in space.
In 2015 and 2016, Portable On Board 3D Printer tested an automated printer developed by the Italian Space Agency to produce plastic objects in space. The investigation provided insight into how the material behaves in microgravity, which could support development of European additive manufacturing technology for use in space.
Printing with other materials

Another approach is recycling plastic - for example, turning a used 3D-printed wrench into a spoon and creating items from the plastic bags and packing foam needed to send supplies to space. This technology could help reduce the amount of raw material at launch and cut down on the volume of waste that must be disposed of on long journeys. The Refabricator, a machine created by Tethers Unlimited Inc, tested this approach and successfully manufactured its first object. Some issues occurred in the bonding process, likely caused by microgravity, but assessment of the material could help determine whether there are limits to how many times plastic can be re-used. Ultimately, researchers plan to create a database of parts that can be manufactured using the space station's capabilities.
Redwire Regolith Print (RRP) tested another kind of feedstock for 3D manufacturing in orbit, a simulated version of regolith, the dust present on the surface of the Moon and other planetary bodies. Results could lead to development of technology for using regolith to construct habitats and other structures rather than bringing raw materials from Earth.
The space station also has hosted studies of a form of 3D printing called biological printing or bioprinting. This process uses living cells, proteins, and nutrients as raw materials to potentially produce human tissues for treating injury and disease, which could benefit future crews and patients on Earth.
Other manufacturing techniques tested on the orbiting lab include producing optical fibers and growing crystals for synthesizing pharmaceuticals and fabricating semiconductors.






