Researchers from the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have leveraged artificial intelligence (AI) to design a novel series of Fe-based amorphous alloys. These materials exhibit both ultra-high saturation magnetization (Bs) and ultra-low coercivity (Hc), offering potential to improve the energy efficiency and performance of high-frequency, high-power electronic devices. The findings were published in Advanced Functional Materials.
As electronics operate at higher frequencies in the MHz and GHz ranges, traditional soft magnetic materials like silicon steel face significant limitations due to high core losses. This leads to reduced efficiency, excessive heat, and risks of thermal runaway, especially in high-power applications like 5G communications and electric vehicles. Fe-based amorphous alloys offer a promising alternative with low coercivity and minimal core losses, but their low saturation magnetization hinders their use in high-power-density devices.
To address these challenges, the research team employed machine learning models to predict and optimize the saturation magnetization of Fe-based amorphous alloys. Among the models tested, the XGBoost algorithm demonstrated superior performance, achieving an R² coefficient above 0.85 and a root-mean-square error below 0.12 T, indicating high predictive accuracy. Feature analysis revealed that iron content (above 75 atomic percent), mixing enthalpy (between -18.7 and -14 kJ/mol), and electronegativity difference (below 0.07) are critical factors in achieving high Bs while maintaining glass-forming ability.
Building on these insights, the researchers introduced cobalt to exploit the Fe-Co exchange coupling effect, designing a series of Fe-based amorphous alloys, including Fe-Co-Ni-Si-B and Fe-Co-Ni-B-P-C. Following magnetic field annealing, these alloys achieved Bs values exceeding 1.85 T, with some reaching up to 1.92 T, and Hc as low as 1.2 A/m. These properties surpass those of conventional silicon steel, positioning the new alloys as promising candidates for high-performance applications.
The advanced Fe-based amorphous alloys hold significant promise for use in smaller, lighter magnetic components within electronic systems. Their enhanced performance could drive innovations in next-generation technologies requiring high power density and minimal thermal waste.
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and other funding agencies.
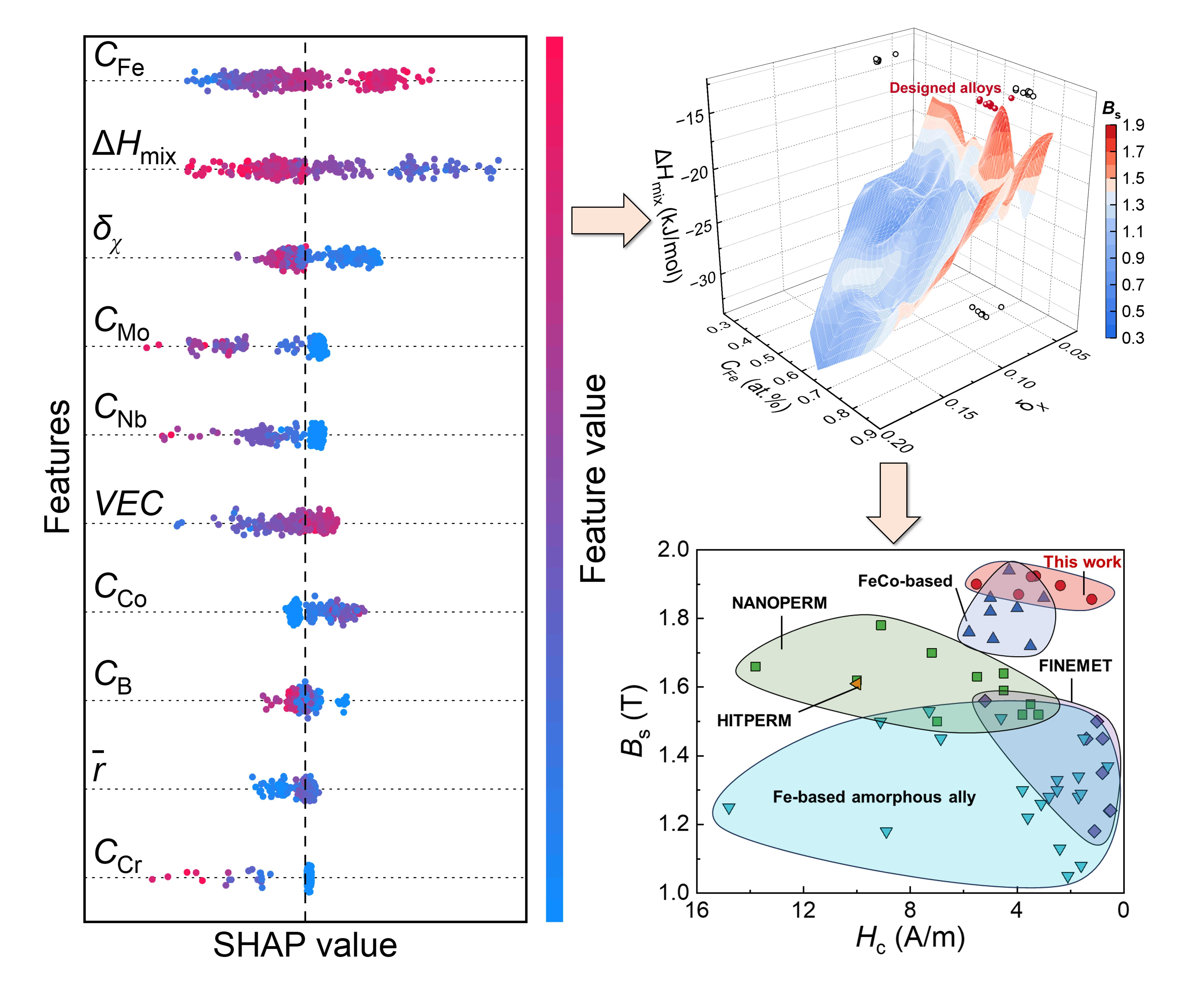
Fig. Fe-based amorphous alloys with high saturated magnetization developed via artificial intelligence (Image by NIMTE)






