UC Davis Health partner hospital Adventist Health and Rideout (AHRO) has dramatically cut the time it takes to transfer stroke patients to specialty care thanks to a new artificial intelligence tool. The Marysville, California hospital launched the new tool, called Viz.ai in May. As a result, AHRO's stroke program reduced what's known as door-in-door-out time from an average of 202 minutes in 2023 to 109 minutes now.
Door-in-door-out time measures how long it takes for a patient to be transferred from one hospital to another for specialty care. It is an important metric, as stroke care is time sensitive.
"Viz.ai has decreased our door-in-door-out times by nearly 50%," said AHRO Chief Medical Officer Alexander Heard. "This not only enhances the speed at which patients receive care but also significantly improves their outcomes. The impact on our stroke patients has been truly transformative."
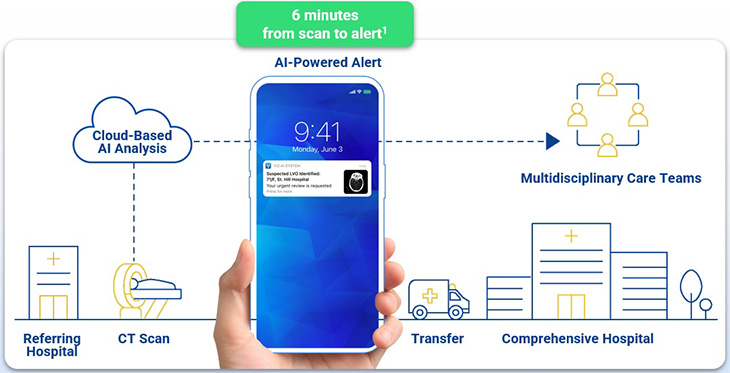
Viz.ai helps streamline care coordination by analyzing a patient's computerized tomography (CT) scan and alerting care teams of a potential stroke within minutes. It is also used by UC Davis Health.
A stroke occurs when a blood clot or burst blood vessel blocks oxygen and nutrients to the brain.
When a potential stroke patient arrives at AHRO, their CT scan is uploaded to the secure Viz.ai platform. Within minutes, the AI analyzes the scan. If it identifies a large vessel occlusion, a major type of stroke, the tool sends mobile notifications to vascular neurologists at both AHRO and UC Davis Health's Comprehensive Stroke Center. Reviewing physicians decide whether or not the patient should transfer to UC Davis Health for more specialized care.
"This AI tool allows for the rapid evaluation of stroke patients with the most severe type of stroke, blockage of a large artery, for interventional treatment," said Director of UC Davis Health's Comprehensive Stroke Center Kwan Ng.
Being able to connect stroke experts at UC Davis Health with ED providers at Rideout rapidly improves access to life-changing treatments and outcomes for stroke patients. Time to treatment is brain saved."-Kwan Ng, director, UC Davis Health's Comprehensive Stroke Center.
The platform complies with federal patient privacy laws.
AHRO's Viz.ai data is preliminary. The hospital has used the technology for ten large vessel occlusion stroke patients since launch in May 2024. In 2023, AHRO had 517 total ED stroke alerts. Tools like Viz.ai may benefit multidisciplinary care teams, especially between different hospitals. The technology removes manual processes and reduces the likelihood that a stroke patient needs to get additional scans.
"Achieving the goal of under 120 minutes, which was previously challenging, has become attainable with the AI technology," said AHRO Stroke Program Manager Caezar Jara. "The partnership with the UC Davis stroke team has streamlined the transfer process for our large vessel occlusion patients."
Regionalizing stroke care is critical. Every minute counts when it comes to a patient's quality of life. The partnership between UC Davis Health and AHRO, combined with tools like Viz.ai, help save lives throughout the region
"Being able to connect stroke experts at UC Davis Health with ED providers at Rideout rapidly improves access to life-changing treatments and outcomes for stroke patients," said Ng. "Time to treatment is brain saved."







