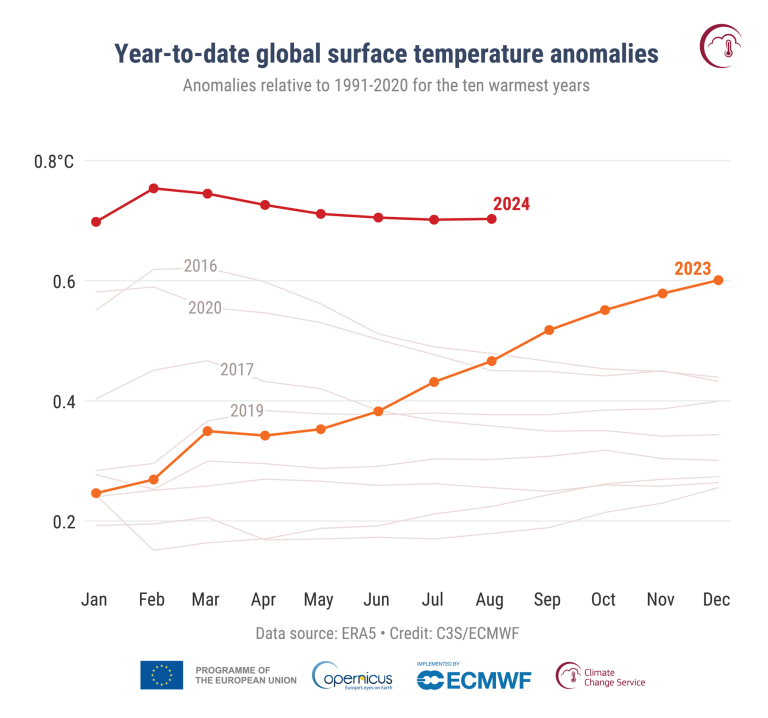
The extended streak of extraordinarily high temperatures has continued, and the year so far has been the warmest on record for the globe, with Africa, Europe and South America each ranking first, according to three leading international datasets.
It was the warmest August on record, marking the 15th consecutive month of record-high global temperatures, which it itself is a record, according to the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and NASA. The European Union's Copernicus Climate Change Service said it was the joint warmest August on record (with August 2023).
The northern hemisphere (boreal) summer was the hottest on record and July saw the hottest day on record. Global temperatures in both July and August 2023 and 2024 were well above anything recorded before.
Global summaries from other international climate centres will be available in the coming days.
WMO combines six international datasets for consolidated rankings for its State of the Climate reports. It will issue the preliminary State of the Global Climate 2024 report for the UN Climate Change conference, COP29, in Azerbaijan in November.
Extreme weather - including intense heat, extreme precipitation and drought - accompanied by floods and wildfires - continued to cause devastation and despair in many countries in August.

With the impacts of climate change increasing constantly, WMO is also intensifying efforts to help protect people from life-threatening weather through the Early Warnings for All Campaign. It is rolling out a new Global Greenhouse Gas Watch initiative to step up support for climate change mitigation.
So far, 2023 is the warmest year on record. Temperatures are just one of the indicators of climate change. Others include ocean heat, sea ice and glaciers.
Global sea ice extent was the second lowest on record in August - with Arctic sea ice being the fourth lowest and Antarctic sea ice the second lowest on record, according to the Copernicus Climate Change Service and NOAA reports.
The global ocean was second warmest on record for August. Near-average sea surface temperatures (SSTs) were observed across most of the equatorial Pacific Ocean, with forecasts suggesting a possible transition to La Niña during NH autumn, but sea surface temperatures across the oceans remained unusually high over many regions.
August temperatures were above average across much of the global land surface except for Alaska, eastern Russia, southern South America, central Africa and west-central Asia.