
During the early summer, corals simultaneously release tiny balls composed of sperms and eggs, known as bundles, that float to the ocean surface. Here the bundles open, allowing the sperm to fertilize the eggs where they eventually settle on the seafloor and become new coral on the reef.
This spectacular annual event is known as "mass-spawning," and usually occurs at night. Although the occurrence of mass-spawning happens around the time of a full moon, it is difficult to predict precisely when. Now, a research team from Tohoku University, Ochanomizu University, and the National Institute for Basic Biology have utilized modeling analysis to indicate that environmental factors act as a determinant in the timing of mass spawning.
"Coral spawning is a complex phenomenon," says Shinchiro Maruyama, an assistant professor at Tohoku University. "It is too complicated to model all the factors involved in a spawning event, so we decided to focus on which day they spawn. Although we know that they spawn a few hours after the dusk, the days can differ according to regions, and even within the same reef."
Maruyama and his team utilized a multidisciplinary approach to address the role of environmental factors, such as temperature; wind speed; and sunlight, to determine the night of spawning, teaming up with specialists in ecology, statistics, physiology, developmental biology, and evolutionary biology. Drawing upon field research, satellite data and literature reviews, they discovered that corals changed the nights of spawning according to the environmental conditions for a period of time before 'the big night.'
Maruyama adds that, "Such fine-tuning for the night of spawning might be advantageous for corals to maximize their chances or meeting future partners in the vast expanses of the ocean."
Coral reefs are a natural treasure of biodiversity in the ocean and understanding mass-spawning gives us further insight into their behavior. Identifying that environmental changes play a role in the mass-spawning timing provides a building block for scientists to address corals behavior going forward.
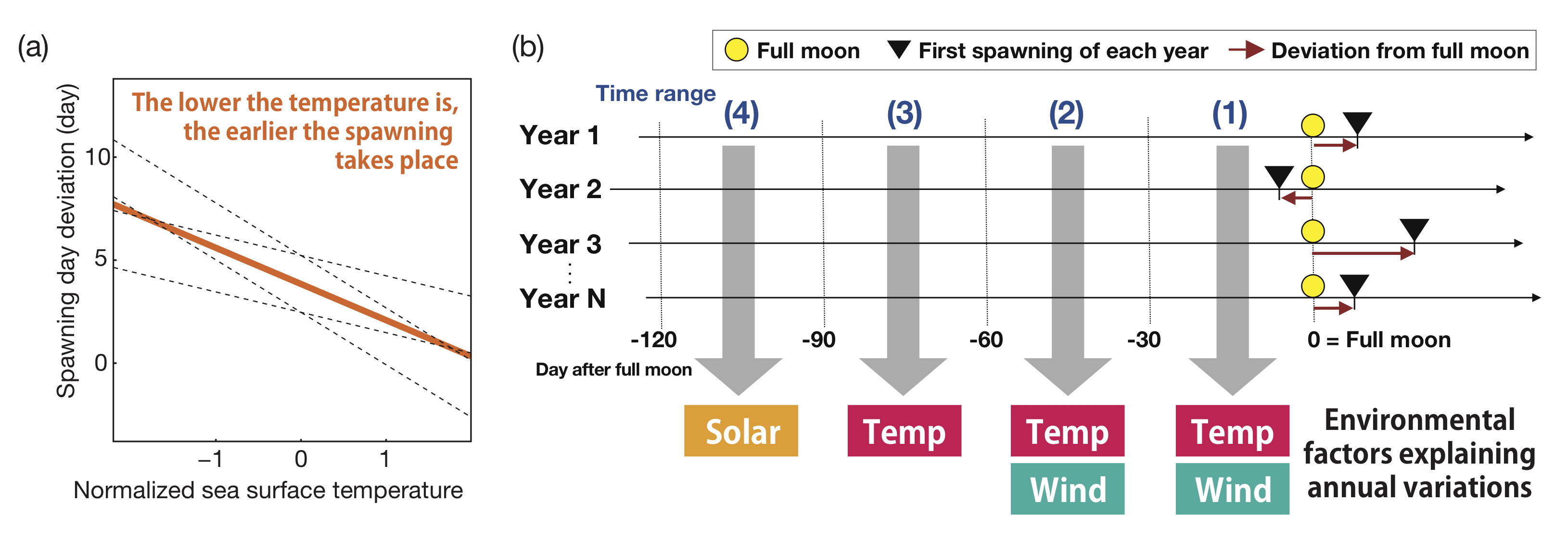
The relationships between environmental factors and deviation between the full moon and the 'first' spawning day of each year. (a) Sea surface temperature well explains the spawning day deviation from the full moon. (b) Distinct environmental factors at each time range are correlated with the spawning day deviation. Solar, solar flux; Temp, sea surface temperature; Wind, wind speed. ⒸModified from Sakai et al.
- Publication Details:
Title: Environmental factors explain spawning day deviation from full moon in the scleractinian coral Acropora
Authors: Yusuke Sakai, Masayuki Hatta, Seishiro Furukawa, Masakado Kawata, Naoto Ueno, Shinichiro Maruyama
Journal: Biology Letters







