When bumblebees move, their vision improves. Scientists at the University of Würzburg have now been able to prove this.
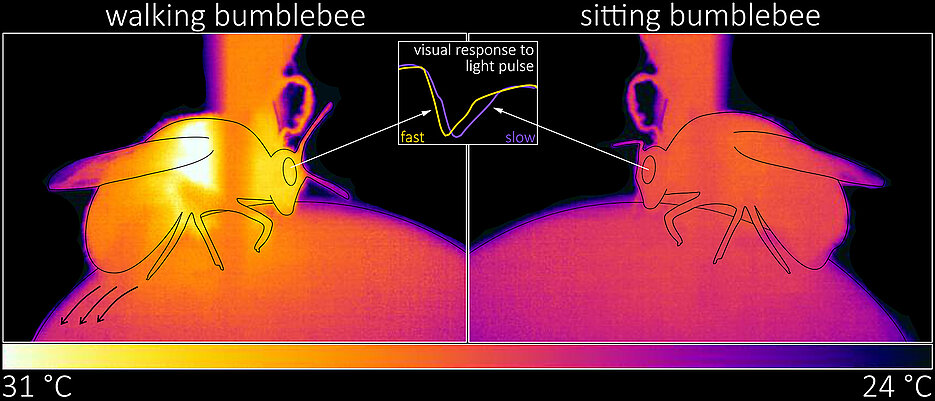
It was already known from other insects that running or flying accelerates the processing of visual information in the brain. However, whether active behavior also has an influence on the processing of stimuli in the eye had not been researched until now.
Using electrophysiological recordings - i.e. measuring and recording electrical activity - a team of researchers from the Julius Maximilians University of Würzburg (JMU) has now determined the reaction speed of the eye of bumblebees while the animals were either sitting or walking. The scientists were able to show that walking bumblebees actually process visual information faster than sedentary ones. They now present their results in the scientific journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
Walking bumblebees see 20 percent faster
"The results were quite remarkable: walking bumblebees see 20 percent faster than their static conspecifics," reports Professor Keram Pfeiffer from the Department of Zoology II at JMU.
Bumblebees are able to actively increase their body temperature and thus also accelerate the course of biochemical processes. To do this, they tremble with their flight muscles. Simultaneous measurement of temperature and eye reaction speed suggested that the observed gain in reaction speed could be a result of increased body temperature. "We were able to prove that this was indeed the case by irradiating sitting animals with a heat lamp and reproducing the results in this way," explains Lisa Rother. The doctoral student is, together with Robin Müller, first author of the study.
It was already known that higher light intensity enables faster vision. In further investigations, the researchers were able to quantify how much brighter the light had to be in order to achieve a similar increase as a result of movement. Result: The light intensity had to be increased by a factor of 14.
Follow-up experiments for deeper insights
Further studies are to clarify what benefit the bumblebees derive from this effect and whether they perhaps even actively use it.
According to Robin Müller, there are basically two possible explanations. The first possibility: "The animals warm up their flight muscles while running so that they can take off at any time. In this case, the observed increase in visual speed would merely be a useful side effect."
The second possibility: the animals actively warm up to process visual stimuli faster. This would have benefits simply because the visually perceived environment changes more rapidly when in motion. So the bumblebees can also process these faster images more quickly. In flight, the bumblebees' head temperature rises to about 35°C. At the same time, the processing time for visual information in the eye would then be only half as long as in a sitting position - which would be fitting for the even greater flood of information in flight.
The research project was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG).
Publication
Walking bumblebees see faster. Lisa Rother, Robin Müller, Erwin Kirschenmann, James J. Foster, Sinan Kaya-Zeeb, Markus Thamm and Keram Pfeiffer. Published: May 17th 2023 https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2023.0460
Video
The video above shows a thermographic image of a bumblebee. At first, the animal is sitting. As soon as it begins to walk, you can see how it warms up, then cools down again when it subsequently sits. In the lower section, the temporal relationship between a light stimulus and the eye's reaction is shown in the form of a so-called cross-correlation. The further the curve shifts to the left, the faster the eye reacts to visual information.






