Most medicines, from aspirin to advanced cancer therapies, are made up of small molecules that move throughout the body, attach to certain proteins and in this way help prevent or treat diseases. However, the binding between these small molecules and their respective proteins usually lasts for a very short period of time, often limiting their beneficial effect.
Dr. Nir London's research group at the Weizmann Institute of Science's Chemical and Structural Biology Department specializes in identifying a special class of molecules - those that stick to proteins throughout the entire span of their short lives, which can last anything from a couple of hours to several days. This particularly "sticky" bond may often improve the molecules' efficiency.

In their recent project, researchers from London's group - in collaboration with Prof. Nathanael Gray from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Prof. Kun Ping Lu from the Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, MA, USA - focused on the Pin1 protein, which for quite some time has been known to play a role in the development of several different types of cancer. Other researchers studying this protein in the past have shown that genetically inhibiting its production can prevent tumors from developing. Yet many attempts to identify relevant molecules that can bind to Pin1 and disrupt its activity, for potential therapies, have been unsuccessful. One of the reasons for this failure is that Pin1 evolved to easily bind to other proteins and is thus characterized by a smooth, flat surface that makes it difficult for small drug-like molecules to attach to it.
Pin1 contributes to the disease's progression in two ways: It supports the activity of other proteins involved in tumor development, and it impedes the work of anticancer proteins. The researchers hypothesized that a molecule that could irreversibly bind to Pin1 may prevent both functions.
To find and identify relevant molecules, the researchers scanned hundreds of potential candidates until they came upon a class of molecules that could bind to Pin1. Based on this result, they designed and produced molecules that are structurally similar to compounds belonging to this class. Out of this group, one particular molecule stood out - it could bind to Pin1 and proved to have no toxic effects on the activities of other proteins, thus making it safe for use.
In their search for the perfect molecule, the researchers also employed methods that made it easier for them to track the irreversible bonds between small molecules and proteins, while testing their behavior in various conditions - in the test-tube, in cell cultures, and in mice. The most effective molecule that was identified was given the name Sulfopin, a combination of sulfolane - a chemical group that characterizes several of the molecules that bind to Pin1 - and the name of the protein itself.
While the effect of Sulfopin is relatively small during the first couple of days posttreatment, after about a week it increases considerably
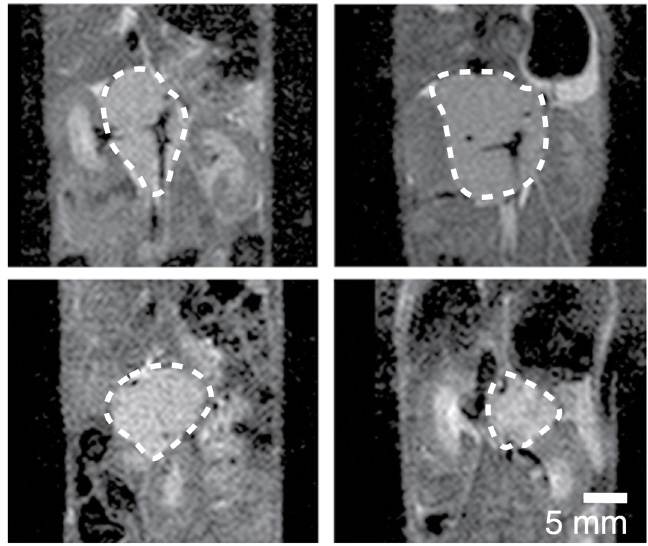
Preliminary studies involving Sulfopin pointed toward which types of cancer might be susceptible to treatment. Based on this finding, the researchers focused on two particular types of cancer: Neuroblastoma - a brain cancer that typically affects children - and pancreatic cancer. Initial experiments conducted in a cell culture showed that while the effect of the molecule is relatively small during the first couple of days posttreatment, after about a week it increases considerably, inhibiting the rate at which the cancer cells divide. To further explore and validate these findings, the researchers used mouse and zebrafish cancer models and showed that Sulfopin significantly inhibited the development of tumors and consequently improved the animals' survival rates.
Realizing the vast potential of Sulfopin, the "Yeda" Research and Development Company, the commercial arm of the Weizmann Institute of Science, patented the molecule, which is already stirring up interest among biotech companies looking to invest in preclinical studies. However, the road to the bedside is long and winding: On average, it takes more than a decade of dedicated research and development efforts, and billion-dollar investments - with very little chance of success - to attain the sought-after title of approved drug for treating cancer.
The study involved researchers from The Institute of Cancer Research, London, UK; Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany; Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, USA; Peking University, Beijing, China; Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA; Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, MA, USA; and Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA.
The study was led by Dr. Christian Dubiella, a postdoctoral fellow from Dr. Nir London's group, and Dr. Benika Pinch, a doctoral student in Prof. Nathanael Gray's group.
Science Numbers
About 800 new cases of neuroblastoma are diagnosed in the United States every year. Close to 50% of these are diagnosed in infants under the age of two years.
Dr. Nir London is the incumbent of the Alan and Laraine Fischer Career Development Chair.
Dr. London's research is supported by the Honey and Dr. Barry Sherman Lab; the Dr. Barry Sherman Institute for Medicinal Chemistry; the Moross Integrated Cancer Center; the Goldhirsh-Yellin Foundation; Nelson P. Sirotsky; Celia Zwillenberg-Fridman; and Israel Englander.






