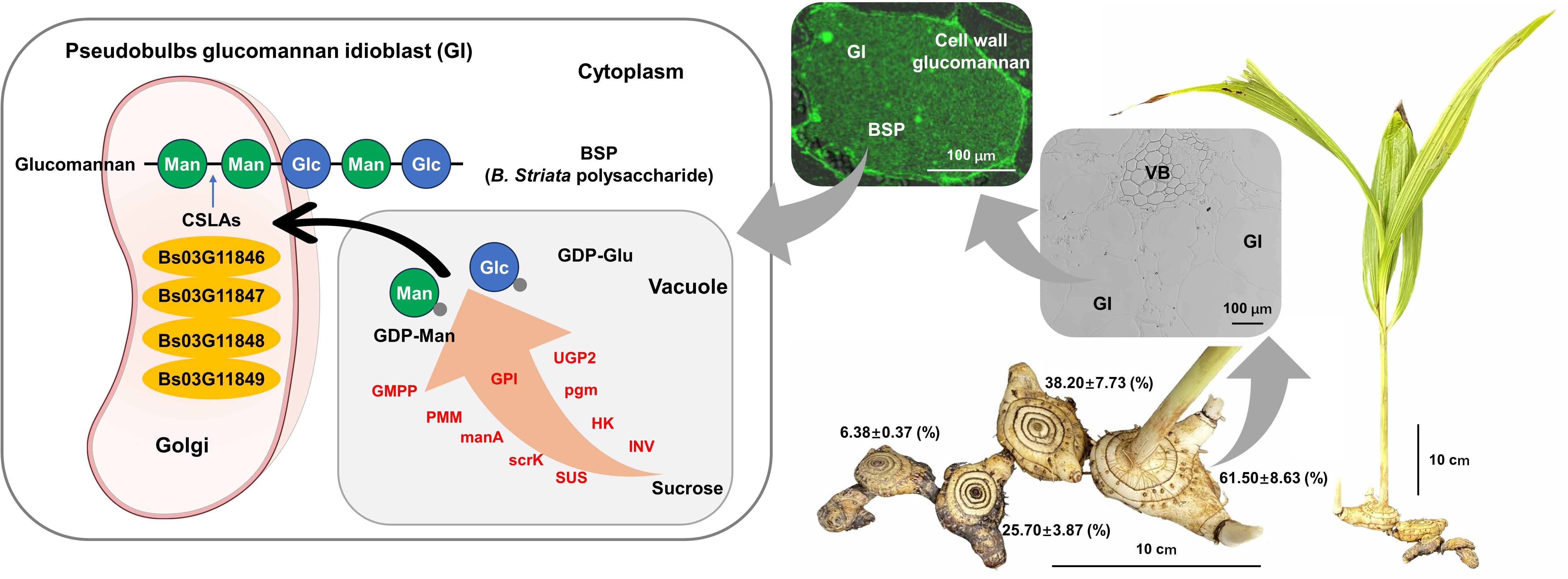
The dry pseudobulb of the plant Bletilla striata Rchb. f. (Orchidaceae), spelled BaiJi in Chinese as an important traditional Chinese medicine, has the effects of astringent hemostasis, detumescence, and promotion of muscle growth. The soluble, non-cellulosic polysaccharide is the main active ingredient of B. striata (BSP) for its hemostatic, antibacterial, antitumor, antifibrotic, wound healing, antioxidant aging, and other medicinal effects. It can also be used as an excellent biopolymer material and pharmaceutical excipient. However, the composition, cytological distribution, and biosynthesis molecular mechanisms of active polysaccharides in Chinese herbs, including BSP, are still poorly understood.
Researchers from the Wuhan Botanical Garden of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) analyzed the content, composition, distribution, and biosynthesis of BSP, obtained candidate enzyme genes involved in BSP biosynthesis, and characterized the cellulose synthase-like family A (CSLA) gene family in the glucomannan polymerization of the cell wall and BSP.
The results show that BSPs are the water-soluble polysaccharides deposited only in the pseudobulb of the medicinal tissue, with a mass ratio of approximately mannose:glucose=3:2, and are distributed in the cytoplasm outside the vacuoles, which can be significantly differentiated from glucomannan in cell wall fractions.
There are 12 enzyme families involved in the biosynthetic pathway from sucrose to glucomannan. They identified the BSP-related genes and suggested that the functional differentiation of the CSLA subfamily may be the key to the flow of glucomannan to intracellular polysaccharides or cell wall hemicellulose fractions. Four CSLA family members of a gene cluster, Bs03G11846, Bs03G11847, Bs03G11848, and Bs03G11849, can form homo- or heterodimers that affect BSP synthesis in the B. striata pseudobulb.
The results provide genetic resources and theoretical basis for the creation, development, and utilization of new and excellent germplasm of B. striata.
This study, entitled "Cytochemical localization and synthesis mechanism of the glucomannan in pseudobulbs of Bletilla striata Reichb. f," was published in Horticulture Research, and it was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Biological Resources Program of CAS.