The Tibet ASγ experiment, a China-Japan joint research project on cosmic-ray observation, has discovered ultra-high-energy diffuse gamma rays from the Milky Way galaxy. The highest energy detected is estimated to be unprecedentedly high, nearly 1 Peta electronvolts (PeV, or one million billion eV).
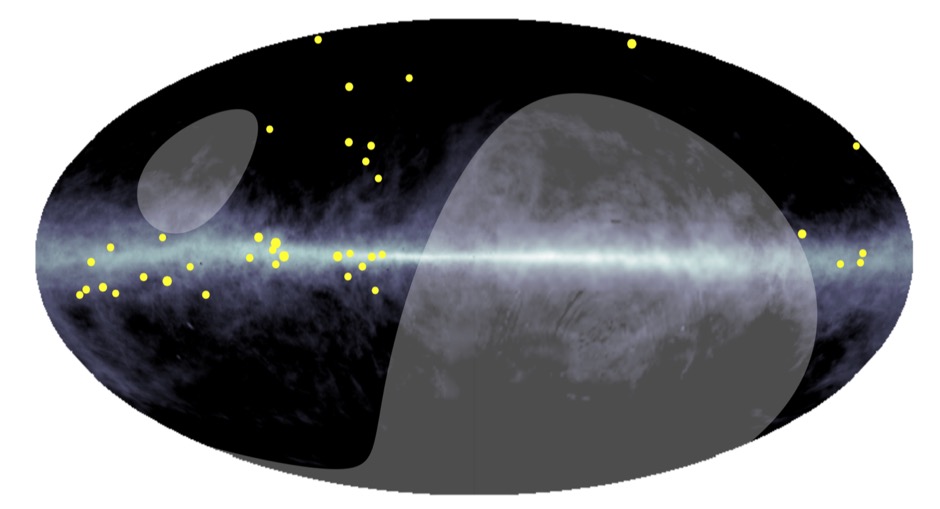
Surprisingly, these gamma rays do not point back to known high-energy gamma-ray sources, but are spread out across the Milky Way (see Fig.1).
Scientists believe these gamma rays are produced by the nuclear interaction between cosmic rays escaping from the most powerful galactic sources ("PeVatrons") and interstellar gas in the Milky Way galaxy. This observational evidence marks an important milestone in revealing the origin of cosmic rays, which has puzzled mankind for more than a century.
However, cosmic rays can interact with the interstellar medium near their acceleration place and produce gamma rays with roughly 10% of the energy of their parent cosmic rays. As the direction of electrically neutral gamma rays cannot be changed by the magnetic field, ultra-high-energy gamma rays (0.1-1 PeV) may tell us where the PeVatrons are in the Milky Way.
The Tibet ASγ experiment was started in 1990. After several expansions, the current air shower array consists of more than 500 radiation detectors distributed across about 65,000 square meters. In order to improve its sensitivity to gamma rays observations, new water Cherenkov-type muon detectors with a total effective area of 3,400 m2 were added under the existing surface cosmic-ray detectors in 2014 (see Fig. 2).
Since gamma-rays events are muon poor and the dominant proton/nucleus events are muon rich, this feature can be used to suppress the background induced by the proton/nucleus events. Using this technique, the Tibet ASγ experiment successfully reduced proton/nucleus background events to one millionth, the most efficient one ever realized in this kind of experiment. We can therefore detect ultra-high-energy gamma rays almost free of cosmic-ray background events.
Scientists from the Tibet ASγ experiment observed gamma rays with energies between about 0.1 and 1 PeV coming from the galactic disk regions. Specifically, they found 23 ultra-high-energy cosmic gamma rays with energies above 398 TeV along the Milky Way. Of these, the highest energy observed was nearly 1 PeV, which is a new world record for gamma ray photons detected anywhere.
Surprisingly, these gamma rays do not point back to the most powerful known high-energy gamma-ray sources, but are spread out along the Milky Way! Scientists soon noticed that these gamma rays probably originated from the interaction of PeV cosmic rays and the interstellar medium after they escaped from the acceleration sources (PeVatrons). This process, known as "hadronic origin," produces gamma rays with energies roughly one-tenth that of their parent cosmic rays via the production and subsequent decay of neutral pions.
These diffuse gamma rays hint at the ubiquitous existence of powerful cosmic particle accelerators (PeVatrons) within the Milky Way. In other words, if PeVatrons exist, the cosmic rays they emit would permeate the galaxy, producing a diffuse glow of gamma rays of extreme energies. That' s just what scientists with the Tibet ASγ experiment have found. This is a long-awaited discovery for decades, providing unequivocal evidence for the existence of PeVatrons in the past and/or now in our Milky Way galaxy.
Two years ago, scientists of the Tibet ASγ experiment found extremely energetic gamma rays from the Crab Nebula, a pulsar wind nebula in the Milky Way. Those gamma rays were probably produced in a different manner, such as by high energy electrons/positrons in the nebula, a process called "leptonic origin."








