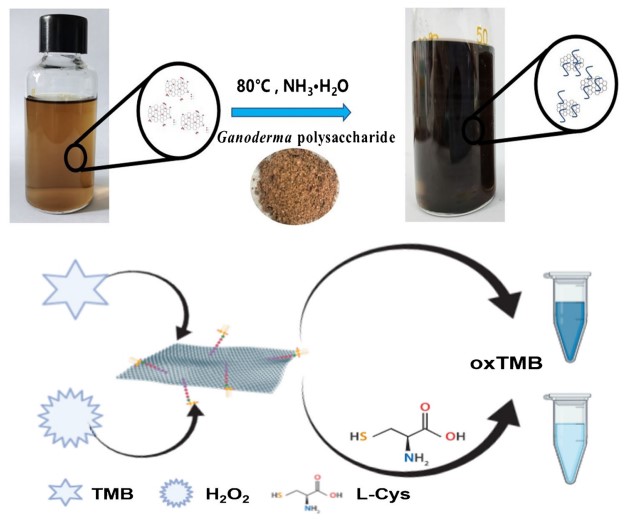
Graphene-based materials can be obtained using various reducing agents, many of which are dangerous and toxic chemicals, and the obtained graphene-based materials are prone to aggregation, limiting their practical applications.
Recently, a research group of Prof. HUANG Qing from the Institute of Intelligent Machines, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), prepared graphene-based nanozymes through a simple and green preparation method, and verified that it can be used to detect L-cysteine in serum.
The study, published in Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
The researchers used Ganoderma lucidum extract polysaccharides as reducing agents and stabilizers to prepare graphene-based materials under mild hydrothermal conditions.
The polysaccharides in Ganoderma lucidum are rich in types and have many excellent biochemical properties. It is proved that Ganoderma polysaccharide can fully reduce graphene oxide, and the existence of Ganoderma polysaccharide can improve the stability and dispersion of graphene-based materials in water.
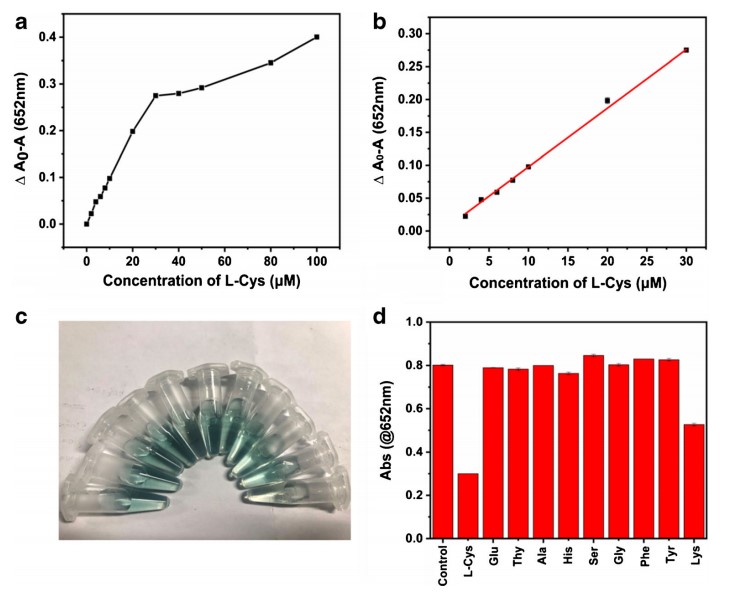
They further studied the catalytic process of the as-synthesized nanozyme, which showed good catalytic activity.
"We developed a colorimetric method for the detection of L-cysteine in serum, an essential amino acid which is involved in protein synthesis, post-translational modification and metabolism," said Prof. HUANG, the corresponding author of the study. "L-cysteine was detected in serum with high sensitivity and selectivity through this method."