6 min read
Artificial intelligence is helping scientists to identify minerals within rocks studied by the Perseverance rover.
Some scientists dream of exploring planets with "smart" spacecraft that know exactly what data to look for, where to find it, and how to analyze it. Although making that dream a reality will take time, advances made with NASA's Perseverance Mars rover offer promising steps in that direction.
For almost three years, the rover mission has been testing a form of artificial intelligence that seeks out minerals in the Red Planet's rocks. This marks the first time AI has been used on Mars to make autonomous decisions based on real-time analysis of rock composition.

The software supports PIXL (Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry), a spectrometer developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. By mapping the chemical composition of minerals across a rock's surface, PIXL allows scientists to determine whether the rock formed in conditions that could have been supportive of microbial life in Mars' ancient past.
Called "adaptive sampling," the software autonomously positions the instrument close to a rock target, then looks at PIXL's scans of the target to find minerals worth examining more deeply. It's all done in real time, without the rover talking to mission controllers back on Earth.
"We use PIXL's AI to home in on key science," said the instrument's principal investigator, Abigail Allwood of JPL. "Without it, you'd see a hint of something interesting in the data and then need to rescan the rock to study it more. This lets PIXL reach a conclusion without humans examining the data."
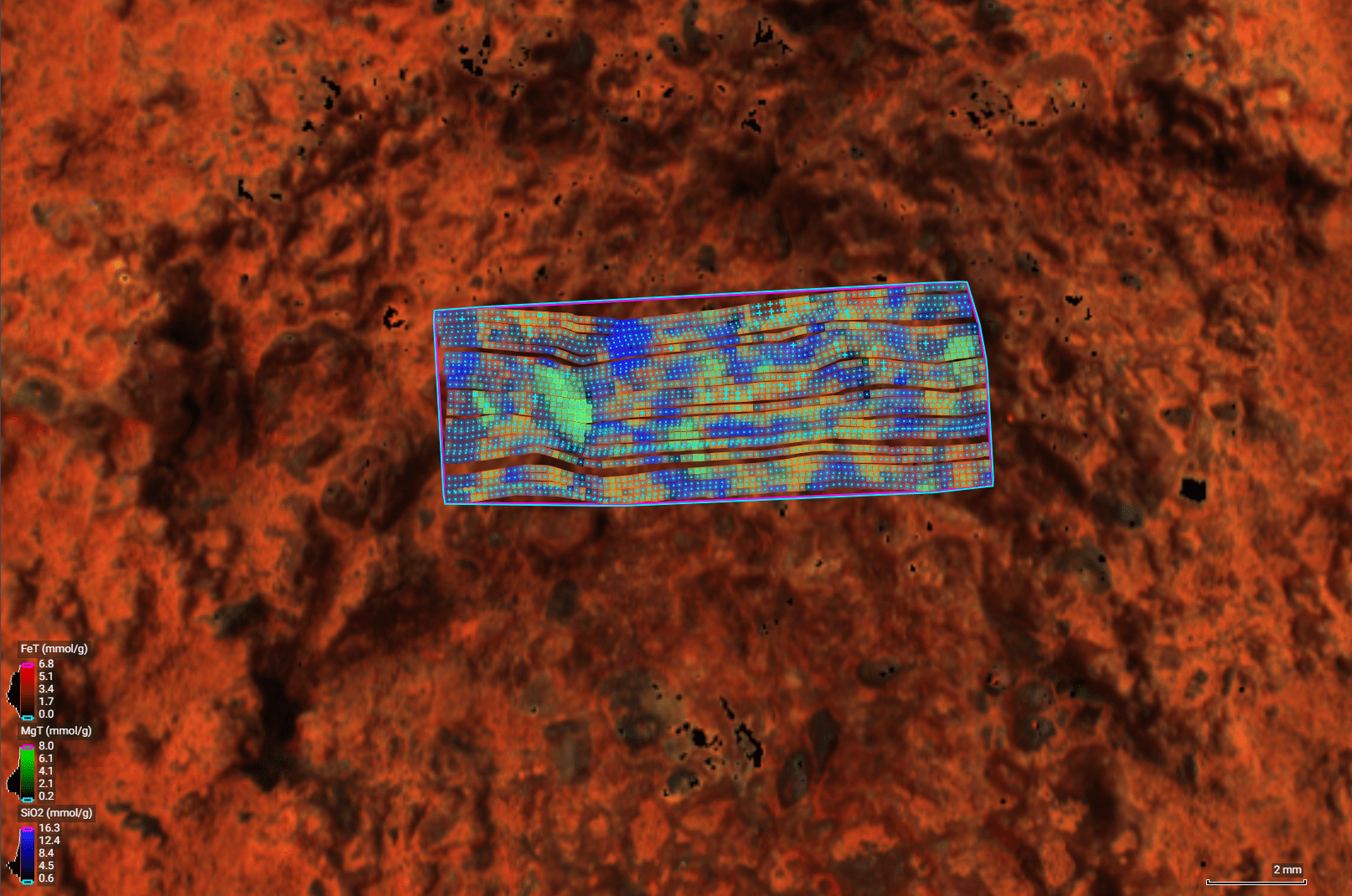
Data from Perseverance's instruments, including PIXL, helps scientists determine when to drill a core of rock and seal it in a titanium metal tube so that it, along with other high-priority samples






