Dozens of species of frogs, salamanders and other amphibians quietly disappeared from parts of Latin America in the 1980s and 2000s, with little notice from humans, outside of a small group of ecologists. Yet the amphibian decline had direct health consequences for people, according to a study from the University of California, Davis.
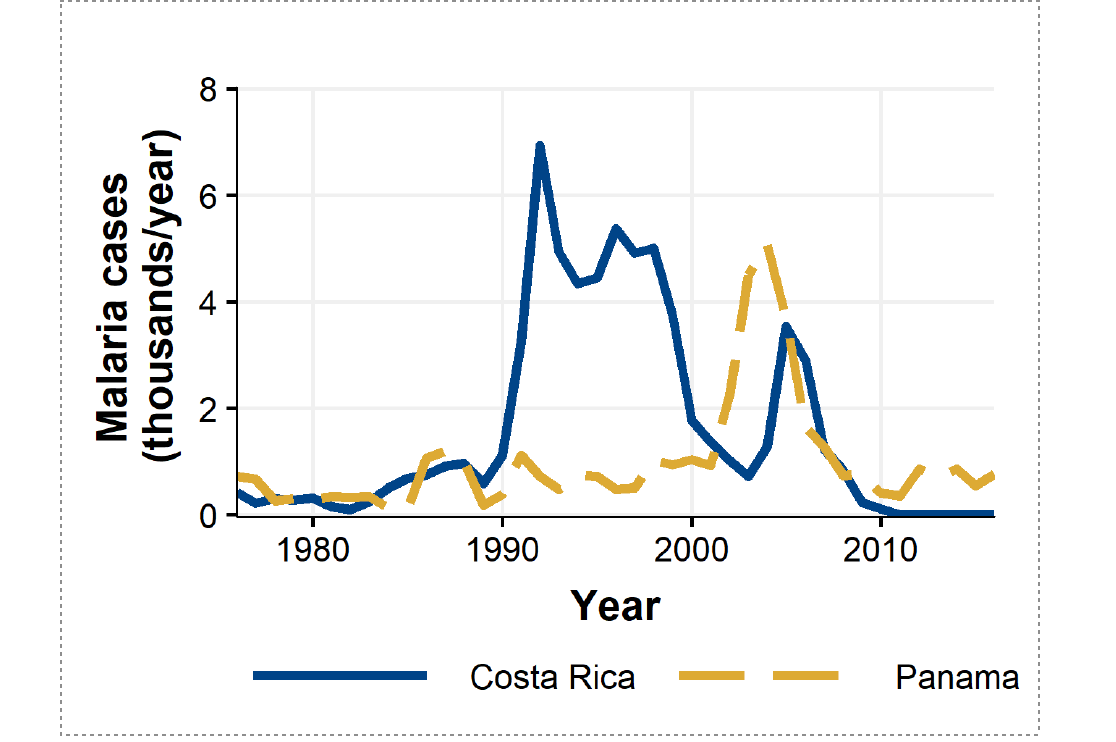
The study, published in the journal Environmental Research Letters, links an amphibian die-off in Costa Rica and Panama with a spike in malaria cases in the region. At the spike's peak, up to 1 person per 1,000 annually contracted malaria that normally would not have had the amphibian die-off not occurred, the study found.
"Stable ecosystems underpin all sorts of aspects of human well-being, including regulating processes important for disease prevention and health," said lead author Michael Springborn, a professor in the UC Davis Department of Environmental Science and Policy. "If we allow massive ecosystem disruptions to happen, it can substantially impact human health in ways that are difficult to predict ahead of time and hard to control once they're underway."
A natural experiment
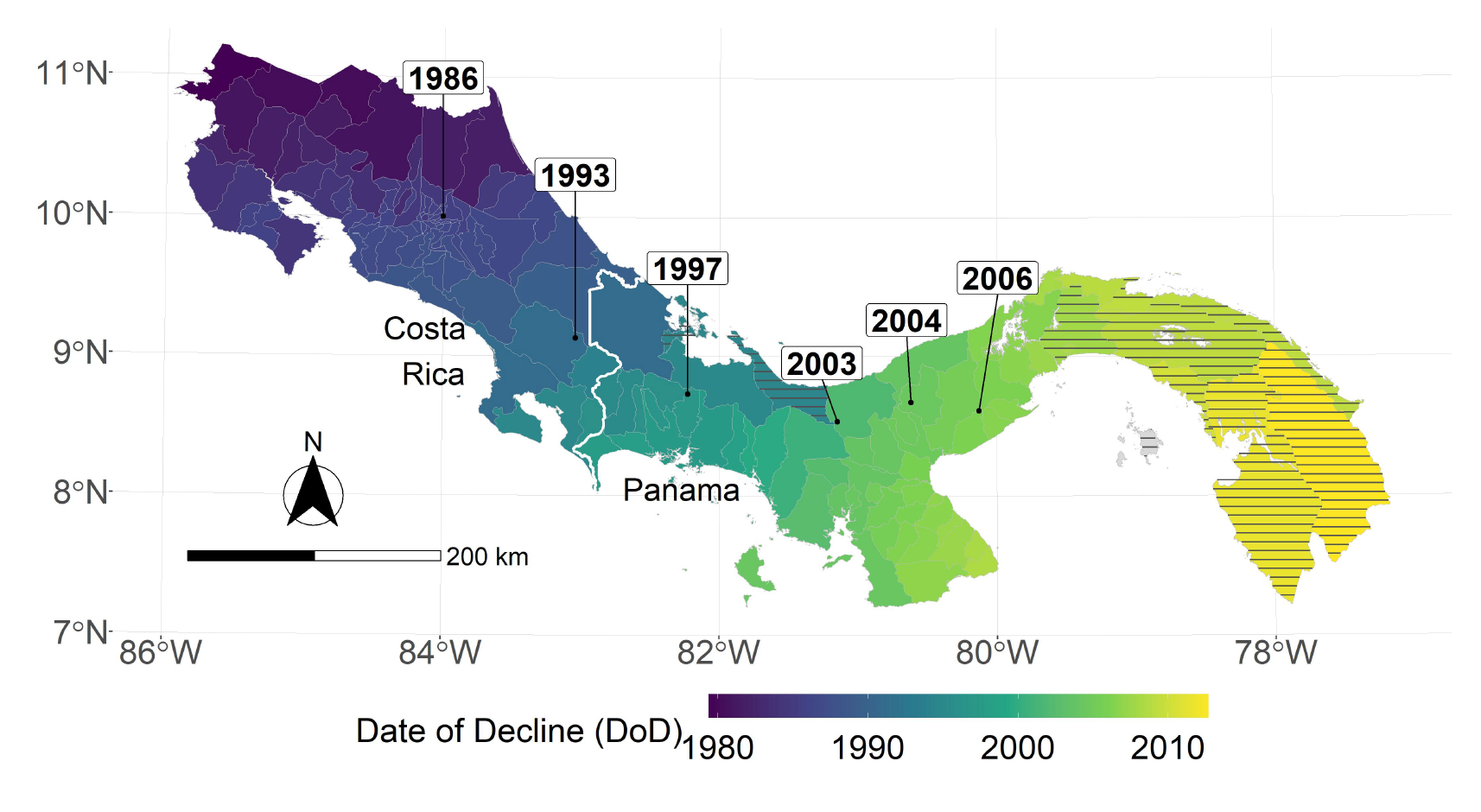
From the early 1980s to the mid-1990s, a deadly fungal pathogen called Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, or "Bd," traveled across Costa Rica, devastating amphibian populations. This amphibian chytrid fungus continued its path eastward across Panama through the 2000s. Globally, the pathogen led to the extinction of at least 90 amphibian species, and to the decline of at least 500 additional species.
Shortly after the mass die-off of amphibians in Costa Rica and Panama, both countries experienced a spike in malaria cases.

Some frogs, salamanders and other amphibians eat hundreds of mosquito eggs each day. Mosquitoes are a vector for malaria. Scientists wondered, could the crash in amphibians have influenced the rise in malaria cases?
To find out, the researchers combined their knowledge of amphibian ecology, newly digitized public health record data, and data analysis methods developed by economists to leverage this natural experiment.
"We've known for a while that complex interactions exist between ecosystems and human health, but measuring these interactions is still incredibly hard," said co-author Joakim Weill, a Ph.D. candidate at UC Davis when the study was conducted. "We got there by merging tools and data that don't usually go together. I didn't know what herpetologists studied before collaborating with one!"
The results show a clear connection between the time and location of the spread of the fungal pathogen and the time and location of increases in malaria cases. The scientists note that while they cannot fully rule out another confounding factor, they found no evidence of other variables that could both drive malaria and follow the same pattern of die-offs.
Tree cover loss was also associated with an increase in malaria cases, but not nearly to the same extent as the loss of amphibians. Typical levels of tree canopy loss increase annual malaria cases by up to 0.12 cases per 1,000 people, compared to 1 in 1,000 for the amphibian die-off.
Trade threats
Researchers were motivated to conduct the study by concerns about the future spread of similar diseases through international wildlife trade. For instance, Batrachochytrieum salamandrivorans, or "Bsal," similarly threatens to invade ecosystems through global trade markets.
Springborn said measures that could help prevent the spread of pathogens to wildlife include updating trade regulations to better target species that host such diseases, as our knowledge of threats evolve.
"The costs of putting those protective measures in place are immediate and evident, but the long-term benefits of avoiding ecosystem disruptions like this one are harder to assess but potentially massive, as this paper shows," Springborn said.
Additional co-authors include Karen Lips of University of Maryland, Roberto Ibáñez of Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute in Panamá, and Aniruddha Ghosh of UC Davis and the Alliance of Biodiversity International and CIAT in Kenya.
The study was funded by the National Science Foundation and the UC Davis Institute of the Environment.






