
Marshall Chief Scientist Provides Valuable Insight into NASA Moonquake Study
By Jonathan Deal
The Moon holds clues to the evolution of Earth, the planets, and the Sun, and a new NASA-funded study is helping scientists better understand some of the mysteries beneath the surface of our nearest cosmic neighbor. The co-author of that study is chief scientist of NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, Renee Weber, who is also a member of NASA's Artemis Science Team - a broad group of scientists from around the agency working to commence a new era of deep space science and exploration.
As a lunar seismologist and lunar geophysicist, Weber provides expertise to the Artemis Science Team, including knowledge of the types of seismic events that can occur on the Moon, to better understand its internal geology and surface environment.
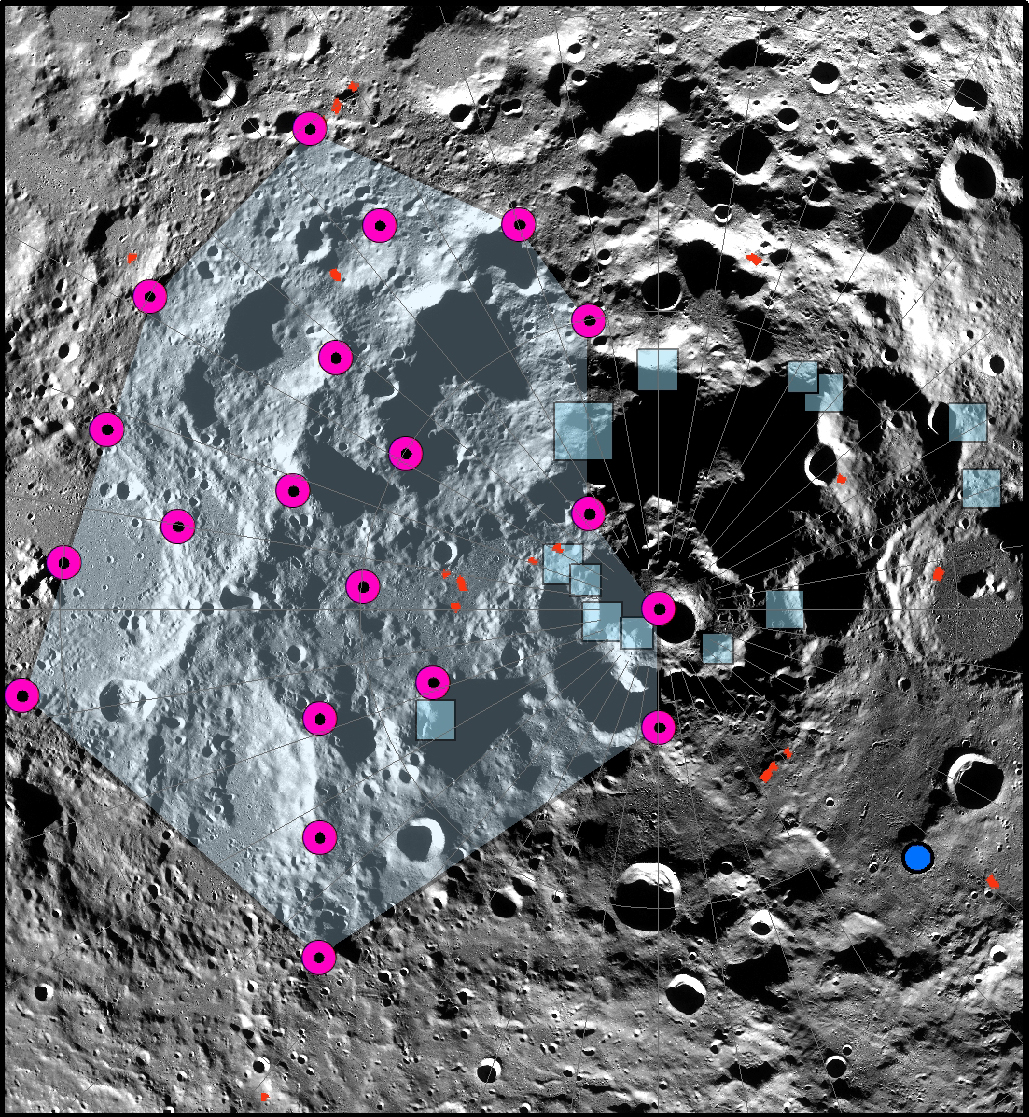
The latest study revealed that the Moon is still geologically active and presents evidence that tectonic faults, generated as the Moon's interior gradually cools and shrinks, are found near some of the areas NASA identified as candidate landing regions for Artemis III - the first Artemis mission planned to have a crewed lunar landing.
"This study looked at tectonic faults and steep slopes in the lunar South polar region and found that some areas are susceptible to seismic shaking and regolith landslides," Weber said. "Once the faults were mapped, we calculated the sizes of potential moonquakes that could be generated to create a map of seismic hazard in the vicinity of tectonic faults and steep slopes."
The study discovered that relatively small, young thrust faults, called lobate scarps, are widely distributed in the lunar crust. The scarps form where contractional forces break the crust and push, or thrust, rock on one side of the fault up and over rock on the other side. The contraction is caused by cooling of the Moon's still-hot interior and tidal forces exerted by Earth, resulting in global shrinking. The scarps were identified in images taken by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera onboard NASA's LRO (Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter).
The formation of the faults is accompanied by seismic activity in the form of shallow-depth moonquakes. Such shallow moonquakes were recorded by the Apollo Passive Seismic Network, a series of seismometers deployed by the Apollo astronauts, and could potentially also be recorded by a new seismic instrument scheduled to launch next year aboard an upcoming CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) flight. That instrument - the Farside Seismic Suite - will return the agency's first seismic data from the far side of the Moon, helping scientists to understand the region's tectonic activity. The data may also reveal how often the lunar far side is impacted by small meteorites and determine if the seismicity is different on the far side of the Moon from what was measured during Apollo on the lunar near side.
"To better understand the seismic hazard posed to future human activities on the Moon, we need new seismic data, not just at the South Pole, but globally," Weber said. "Missions like the upcoming Farside Seismic Suite, as well as future potential missions like the Lunar Geophysical Network concept, will expand upon measurements made during Apollo and add to our knowledge of global seismicity."

As NASA develops long-term infrastructure on the lunar surface, Weber's research will provide invaluable insight for the Artemis Science Team that will be refining mission architectures that preserve flexibility for science and operations at a variety of landing sites and will apply new scientific knowledge, such as continued research on seismic measurements, gathered along the way.
"Being able to go back to the Moon, gather more data, and pick up more samples will help us improve our understanding of the Moon and answer our fundamental questions - how did it form? How did it evolve? Where are the resources? More seismic measurements like the ones conducted during Apollo could help us better characterize seismicity in the lunar South Pole region," Weber said.
The study does not impact the Artemis III landing region selection process, according to Weber, because estimating how often a specific region experiences a moonquake is difficult to do accurately, and like earthquakes, scientists can't predict moonquakes. Additionally, for a shorter duration mission like Artemis III, the likelihood of experiencing hazards due to seismic shaking is much lower.
As NASA develops long-term infrastructure, the agency will identify potential regions for where different elements can be established closer to the dates of future Artemis missions. In this site selection process, some of the factors for consideration could be geographic characteristics such as proximity to tectonic features and terrain, making Weber's research all the more valuable.
Deal is a public affairs officer with Marshall's Office of Communications.
Solar Sail Technology Passes Crucial Deployment Test
By Wayne Smith
In his youth, NASA technologist Les Johnson was riveted by the 1974 novel "The Mote in God's Eye," by Jerry Pournelle and Larry Niven, in which an alien spacecraft propelled by solar sails visits humanity. Today, Johnson and a NASA team are preparing to test a similar technology.
NASA continues to unfurl plans for solar sail technology as a promising method of deep space transportation. The agency cleared a key technology milestone in January with the successful deployment of one of four identical solar sail quadrants. The deployment was showcased Jan. 30 at Redwire Corp.'s new facility in Longmont, Colorado. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center leads the solar sail team, comprised of prime contractor Redwire, which developed the deployment mechanisms and the nearly 100-foot-long booms, and subcontractor NeXolve, of Huntsville, which provided the sail membrane. In addition to leading the project, Marshall developed the algorithms needed to control and navigate with the sail when it flies in space.
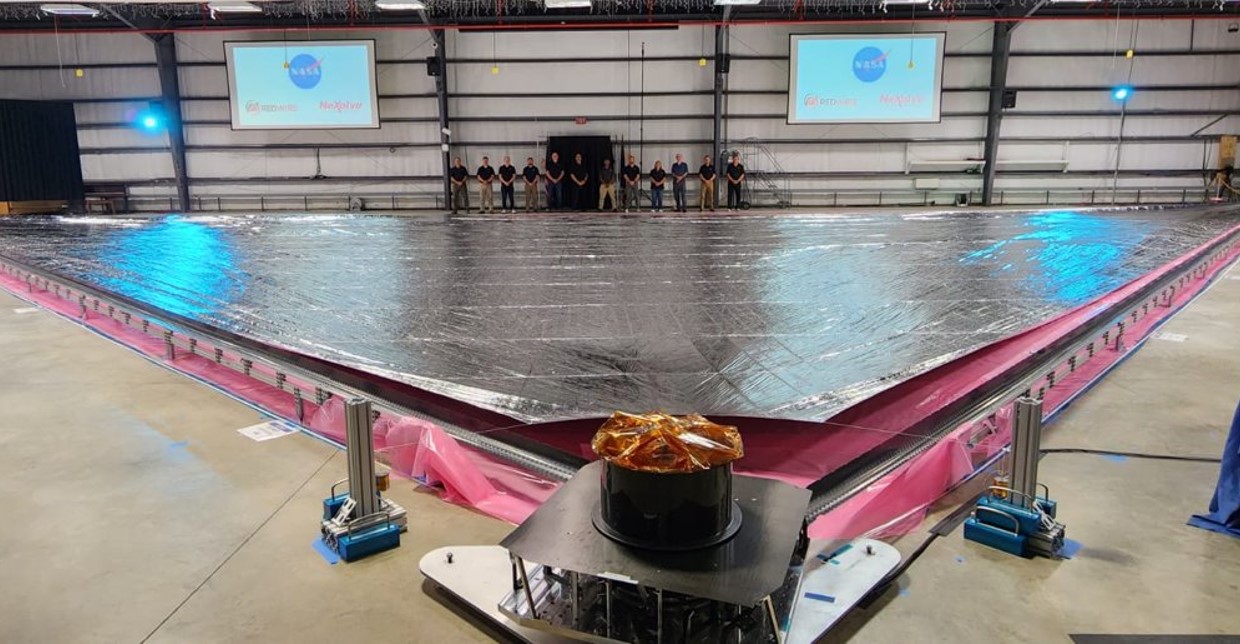

The sail is a propulsion system powered by sunlight reflecting from the sail, much like a sailboat reflects the wind. While just one quarter of the sail was unfurled in the deployment at Redwire, the complete sail will measure 17,780 square feet when fully deployed, with the thickness less than a human hair at 2 and a half microns. The sail is made of a polymer material coated with aluminum.
NASA's Science Mission Directorate recently funded the solar sail technology to reach a new technology readiness level, or TRL 6, which means it's ready for proposals to be flown on science missions.
"This was a major last step on the ground before it's ready to be proposed for space missions," Johnson, who has been involved with sail technology at Marshall for about 25 years, said. "What's next is for scientists to propose the use of solar sails in their missions. We've met our goal and demonstrated that we're ready to be flown."
A solar sail traveling through deep space provides many potential benefits to missions using the technology because it doesn't require any fuel, allowing very high propulsive performance with very little mass. This in-space propulsion system is well suited for low-mass missions in novel orbits.
"Once you get away from Earth's gravity and into space, what is important is efficiency and enough thrust to travel from one position to another," Johnson said.
Some of the missions of interest using solar sail technology include studying space weather and its effects on the Earth, or for advanced studies of the north and south poles of the Sun. The latter has been limited because the propulsion needed to get a spacecraft into a polar orbit around the Sun is very high and simply not feasible using most of the propulsion systems available today. Solar sail propulsion is also possible for enhancing future missions to Venus or Mercury, given their closeness to the Sun and the enhanced thrust a solar sail would achieve in the more intense sunlight there.
Moreover, it's the ultimate green propulsion system, Johnson said - as long as the Sun is shining, the sail will have propulsion. Where the sunlight is less, he envisions a future where lasers could be used to accelerate the solar sails to high speeds, pushing them outside the solar system and beyond, perhaps even to another star. "In the future, we might place big lasers in space that shine their beams on the sails as they depart the solar system, accelerating them to higher and higher speeds, until eventually they are going fast enough to reach another star in a reasonable amount of time."






