6 min read
The space telescope will detect over 100 colors from hundreds of millions of stars and galaxies. Here's what astronomers will do with all that color.
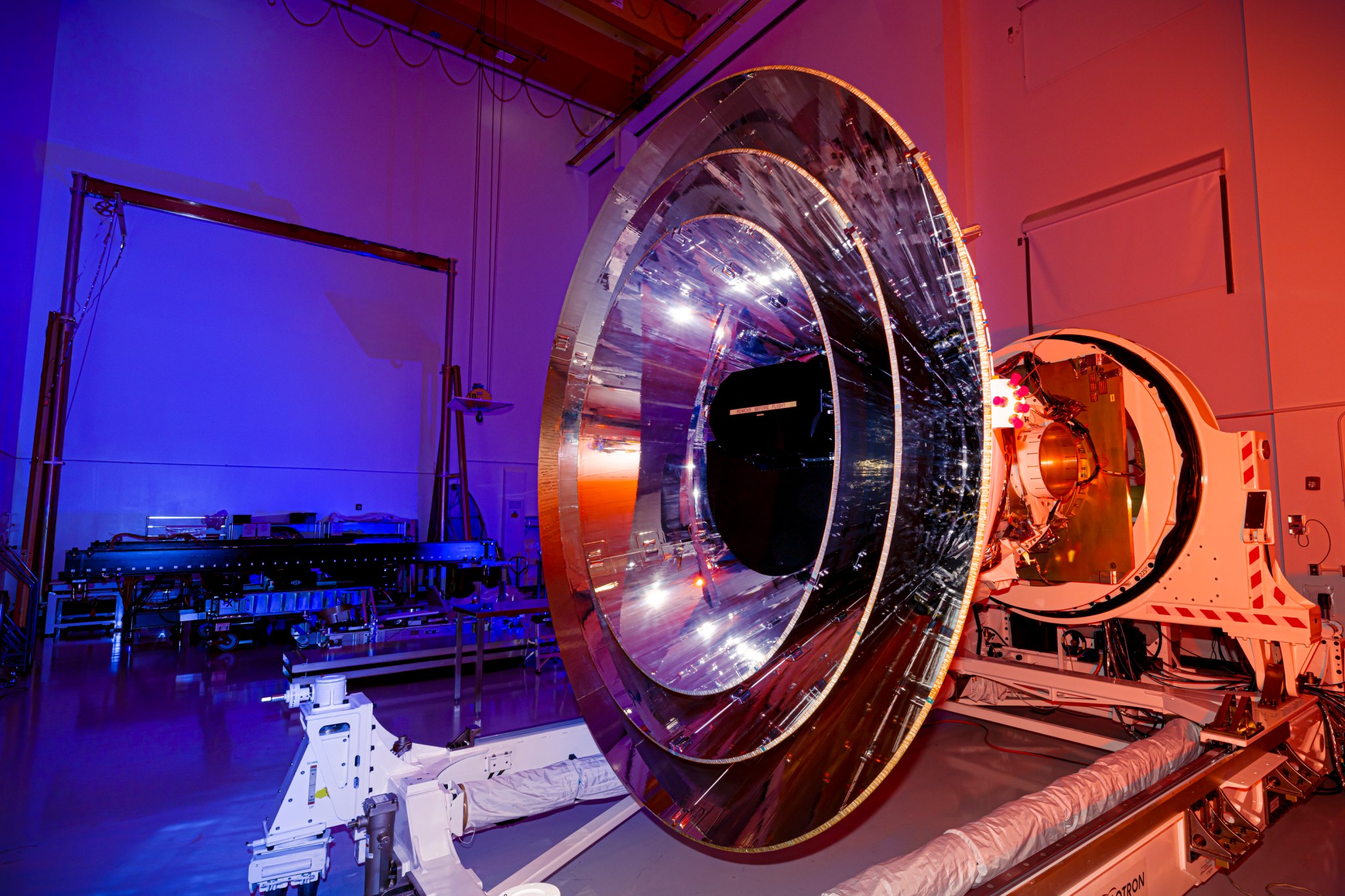
NASA's SPHEREx mission won't be the first space telescope to observe hundreds of millions of stars and galaxies when it launches no later than April 2025, but it will be the first to observe them in 102 colors. Although these colors aren't visible to the human eye because they're in the infrared range, scientists will use them to learn about topics that range from the physics that governed the universe less than a second after its birth to the origins of water on planets like Earth.
"We are the first mission to look at the whole sky in so many colors," said SPHEREx Principal Investigator Jamie Bock, who is based jointly at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Caltech, both in Southern California. "Whenever astronomers look at the sky in a new way, we can expect discoveries."
Short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will collect infrared light, which has wavelengths slightly longer than what the human eye can detect. The telescope will use a technique called spectroscopy to take the light from hundreds of millions of stars and galaxies and separate it into individual colors, the way a prism transforms sunlight into a rainbow. This color breakdown can reveal various properties of an object, including its composition and its distance from Earth.






