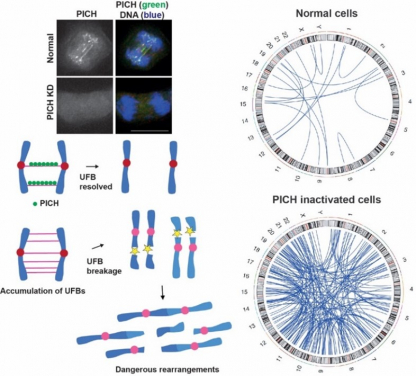
Image 1. PICH acts like a lookout, spotting and attaching to tiny DNA threads called ultrafine anaphase bridges (UFBs). When PICH is inactivated (knockdown, KD), more of these threads form and break, leading to dangerous DNA rearrangements that can be identified by whole genome sequencing. The blue lines in the circular diagrams indicate sites of genomic rearrangements, often involving interchromosomal fusions—a hallmark of tumourigenesis that drives cancer development. Image adapted from Kong et al, Nucleic Acids Research (2024)
Researchers at The University of Hong Kong (HKU) have made an exciting discovery about how human cells protect DNA during cell division, offering new insights into combating diseases such as cancer.
Led by Professor Gary Ying Wai CHAN from the School of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, and Professor Ken Hoi Tang MA from the Department of Pathology, LKS Faculty of Medicine, the research uncovers the vital role of a protein called PICH in preventing genetic errors that can lead to diseases such as cancer. Their findings were recently published in the journal Nucleic Acids Research.
Ultrafine Anaphase Bridges – A Hidden Threat to Our Genome
Every time a cell divides, it must ensure that its DNA is accurately copied and split between the two new cells. However, tiny threads of DNA, known as ultrafine anaphase bridges (UFBs), can sometimes form and cause problems if not properly managed. These UFBs can be thought of as invisible enemies that tangle up our genetic material.
Through their research, the HKU team discovered that the protein PICH acts like a radar, detecting these UFBs and helping to resolve them. They found that when PICH is missing or not functioning properly, cells experience severe genetic damage, including broken DNA, the formation of small DNA-containing structures called micronuclei, and activation of the cell's emergency response systems, which ultimately leads to cell death. Moreover, their findings revealed that such damage can trigger rearrangements of chromosomes—hallmarks of cancer.
PICH prevents dangerous rearrangements of DNA
Building on these findings, the team further investigated the role of PICH in maintaining genetic stability. They found that without PICH, cells not only suffer from severe DNA damage but also accumulate significant genetic errors. A mutated version of PICH that cannot recruit other helper proteins provides only partial protection, while a completely inactive version of PICH fails to resolve UFBs, resulting in even more extensive genetic damage. PICH's activity is crucial for breaking down these DNA threads and preventing genetic chaos. Notably, when PICH is missing, genetic errors are more likely to occur in non-centromeric regions of the DNA due to the breakage of UFBs, leading to dangerous chromosome rearrangements that can cause disease.
Their research proposes that PICH protects human DNA through two key mechanisms. First, it assists another protein, topoisomerase IIα (TOP2A), in untangling the DNA threads. Second, it works with a protein called BLM helicase to convert tangled threads into a simpler, more manageable form. Together, these two actions ensure that DNA threads are properly resolved, preventing genetic errors that could lead to cancer.
"Our research shows how vital PICH is in protecting our DNA from damage during cell division. By understanding how PICH works, we can explore new ways to treat cancers such as colorectal, gastric and breast cancer, which are strongly linked to a high degree of chromosomal instability," said Professor Gary Ying Wai Chan, one of the corresponding authors of the paper.
"Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a powerful tool for detecting genomic instability in diseases such as cancer. In our research, we used NGS to identify mutations in cells lacking PICH, demonstrating its effectiveness in uncovering genetic errors. This productive collaboration with Professor Chan has highlighted the importance of teamwork in scientific research," added Professor Ken Hoi Tang Ma, another corresponding author of the study.
This study highlights the critical role of PICH in maintaining the integrity of human genetic material. Understanding how PICH works opens new possibilities for developing treatments for diseases caused by genetic instability, such as cancer. "By targeting pathways involving PICH, we may be able to develop new therapies to prevent or treat these conditions," explained Professor Gary Ying Wai Chan.
The findings are detailed in the paper 'The Interplay of the Translocase Activity and Protein Recruitment Function of PICH in Ultrafine Anaphase Bridge Resolution and Genomic Stability', published in the journal Nucleic Acids Research.
The full paper can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae1249






