A new U. of I. study uses the Champaign-Urbana Mass Transit District as a case study to identify examples of inequity in mass transit accessabilty within marginalized communities.
Photo by Fred Zwicky
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Public transit systems offering broad coverage of stops and routes may still underserve the communities that rely on them the most, according to a new University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign study.

Dale Robbennolt
Photo courtesty Dale Robbennolt
The study, by former civil and environmental engineering student Dale Robbennolt and Applied Research Institute senior research scientist Ann-Perry Witmer, applies contextual engineering to help determine lapses in equity in public bus transportation access using data from the Champaign-Urbana Mass Transit District as a case study.
The findings are published in the journal Transportation Research Record.

Ann-Perry Witmer
Photo courtesy Ann-Perry Witmer
"Transit authorities tend to focus on the needs of existing users – those who live in high population density areas and travel at peak times," Robbennholt said. "However, people without vehicles, who work unconventional shifts or rely on bus transit for spontaneous, unplanned trips are at a significant disadvantage – especially in low-income areas."
Instead of using ridership surveys and mapping to measure accessibility – like previous studies – Robbennolt created a geographic information system-based tool that evaluates travel times by location, overlaid by block groups defined by economic conditions such as the percentage of people living below the poverty line and those without a vehicle.
The team found that even though CUMTD offers many bus stops in all areas of town, the frequency and timing of routes leave behind some riders and potential riders.
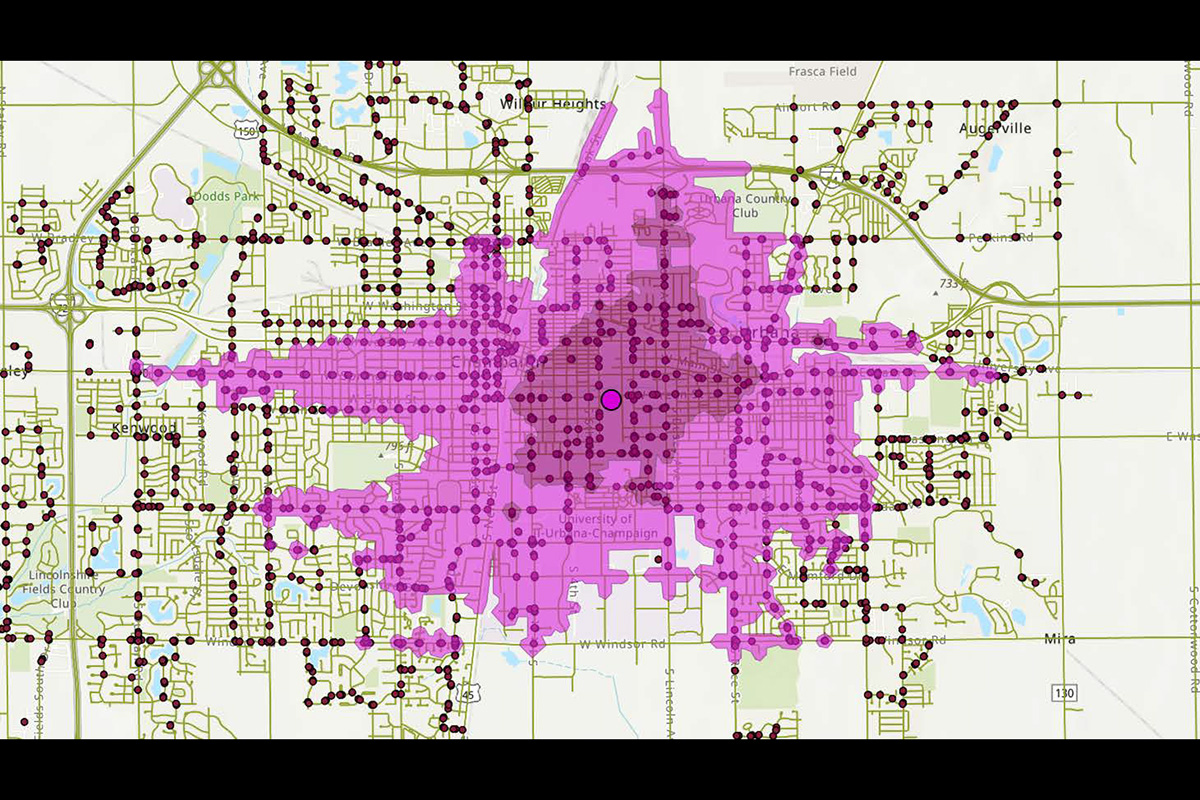
This figure shows an example of the distances within the CUMTD service area that a rider can travel within 15 or 30 minutes.
Graphic courtesy Dale Robbennolt and Ann-Perry Witmer
One hurdle the researchers encountered is that CUMTD services a community with many low-income college students, so differentiating between families living under the poverty line versus low-income college students was vital.
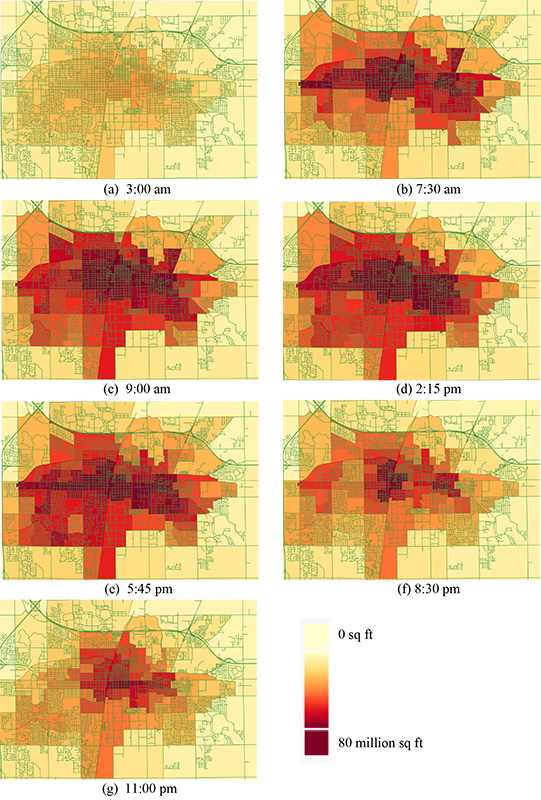
This figure shows the relative accessibility of each block of the CUMTD service area at seven selected times. The maps highlight how daytime service is concentrated around the U. of I. campus and downtowns areas, benefiting people working a regular daytime shift. Accessibility drops in the evening and may pose challenges for those operating on late-night and off-peak schedules, and those who need to make spontaneous trips.
Graphic courtesy Dale Robbennolt and Ann-Perry Witmer
"There is support for CUMTD by the university to provide student transportation, so we see that accessibility is high in the heavily student-oriented block groups, even if the income level is lower," Robbennolt said. "But when you remove those block groups from the data, that trend goes away."
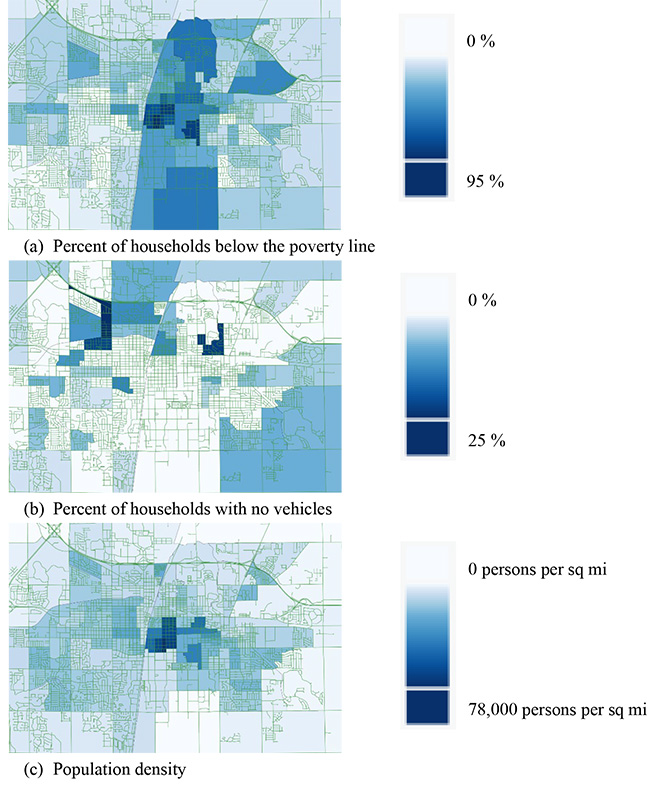
This figure shows the block group characteristics of the CUMTD service area based on the American Community Survey. The highest poverty areas shown in the figure were those in the U. of I. campus, which were well served by the transit system. This map highlights how areas – outside of the campus area – with a high poverty rates have low accessibility compared with the areas immediately around them.
Graphic courtesy Dale Robbennolt and Ann-Perry Witmer
Robbennolt and Witmer said they envision this work as a policymakers' road map for finding and engaging with the community members currently left out of public transit decision-making.
"Ridership surveys don't reach the people left out, and this is where the concept of contextual engineering really comes into this study," Witmer said. "Dale did a fabulous job tracking down the right information and recognizing that just because you see a lot of bus shelters doesn't mean that people have access."
Witmer also is a lecturer in agricultural and biological engineering at Illinois.






