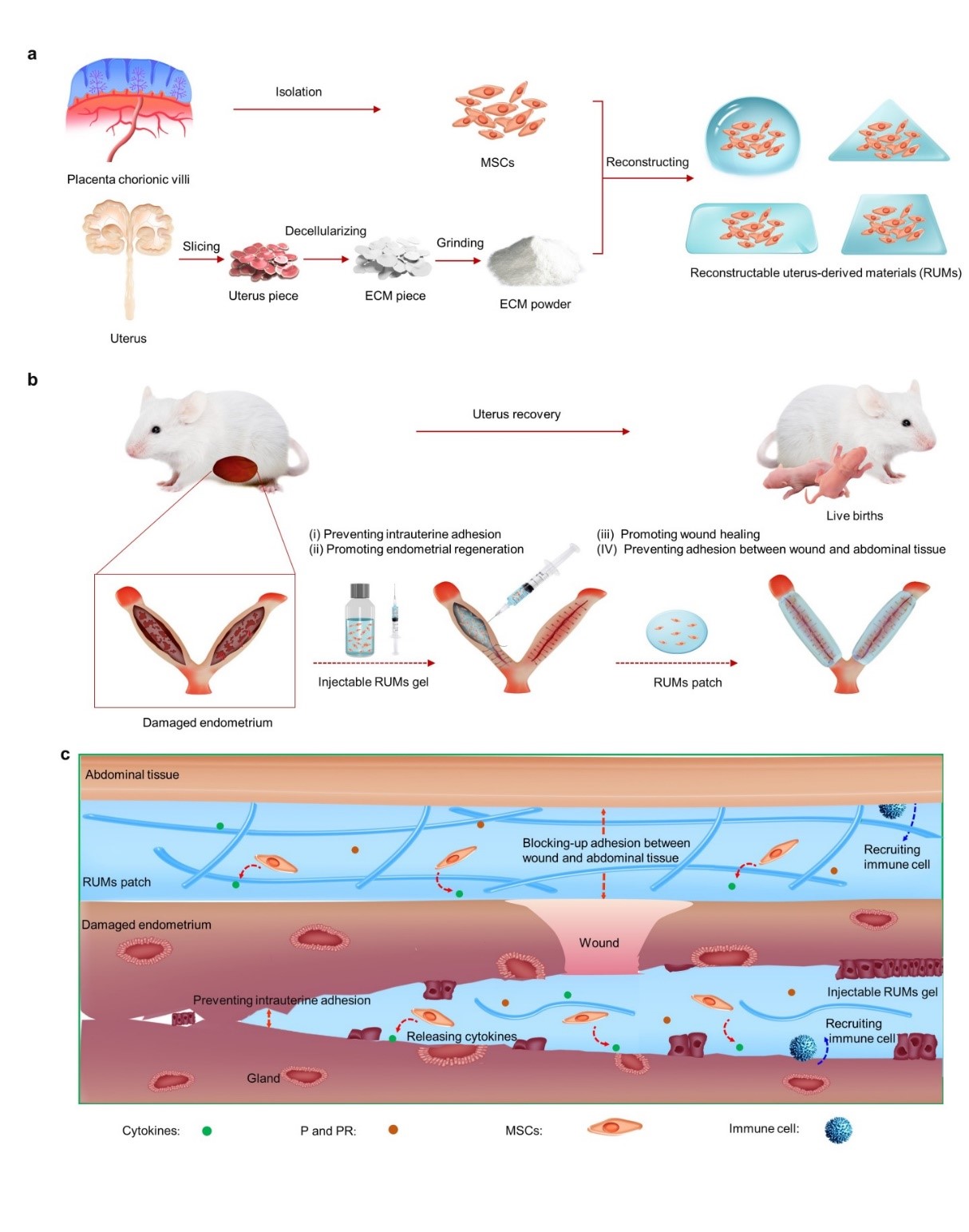
Chinese researchers have demonstrated new reconstructable uterus-derived materials (RUMs) that allow almost complete recovery from severe uterine injury. Relevant results were published online in Advanced Materials.
Using the RUMs, the researchers from the Southern Medical University and the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry (TIPC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences nearly restored the severely damaged uterus of rats, thus supporting normal pregnancy and live birth.
Nowadays, uterine factor infertility is increasingly prevelant, and intrauterine adhesion is the major cause. Current clinical strategies such as hysteroscopic transcervical resection of adhesion, physical barriers (contraceptive devices and intrauterine balloons), and even hormone drugs remain ineffective in repairing uteruses damaged by intrauterine adhesion.
In this research, the researchers fabricated RUMs by seeding chorionic villi mesenchymal stem cells into a uterus-derived extracellular matrix (ECM). Different from traditional ECM scaffolds, the RUMs can be formed into different states (liquid state or solid state) and shapes (cuboidal, triangular-prismatic and cubical) to meet different needs. According to the structural feature of the uterus, the injectable RUM gel and RUM patches can be fabricated for the recovery of damaged uterus.
The uterus is a hollow muscle organ composed of the endometrium, myometrium and perimetrium. The injectable RUM gel acts as a natural barrier to entering the endometrial cavity and can prevent intrauterine adhesion. It promotes angiogenesis, endometrial regeneration, and the rebuilding of muscle collagen.
The RUM patch is applied to the uterine wall to speed up wound healing. During this process, RUMs secretes a variety of cytokines and signaling molecules to improve the damaged microenvironment and promote uterine recovery.
After recovery from treatment, the rat uteruses can support normal pregnancy, fetal development, and live birth as in normal rats.
In addition, about 15.2 g of ECM powder can be produced from a pig uterus. This is enough to treat about 380 rats with severe uterine injury and suggests great prospects for clinical application.
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.