Abstract
A research team, led by Professors Tae-Hyuk Kwon and Duyoung Min from the Department of Chemistry at UNIST, has achieved a significant breakthrough in the battle against cancer through the utilization of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated via water oxidation. In this innovative approach, photosensitisers are employed to produce ROS, which in turn target and oxidise membrane proteins within cancer cells, ultimately leading to their demise.
Throughout their study, the research team identified an amphiphilic photocatalyst that localizes in intracellular membranes to induce oxidative damage to membrane proteins, triggering a form of cell death, known as non-canonical pyroptosis. Unlike the well-known programmed cell death pathway of apoptosis, pyroptosis induces a vigorous inflammatory response and prompts an adaptive immune reaction.
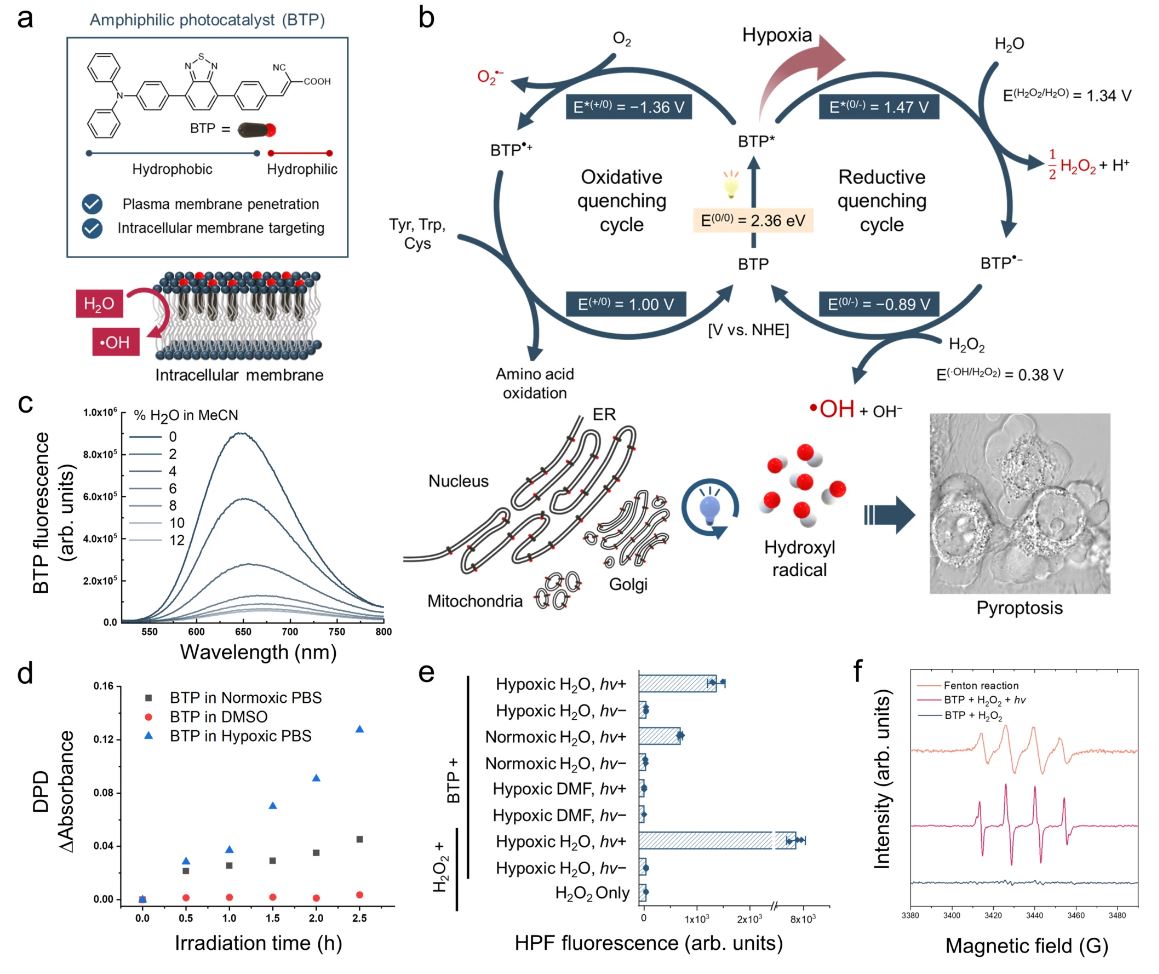
Figure 1. Photocatalytic cycles of amphiphilic photocatalyst (BTP) for inducing pyroptosis via membrane oxidation.
Professor Min highlighted the detrimental effects of protein oxidation on cell membranes, stressing its crucial role in the induction of pyroptosis. This groundbreaking treatment induces an overload on the endoplasmic reticulum within the cell, consequently causing cell death.
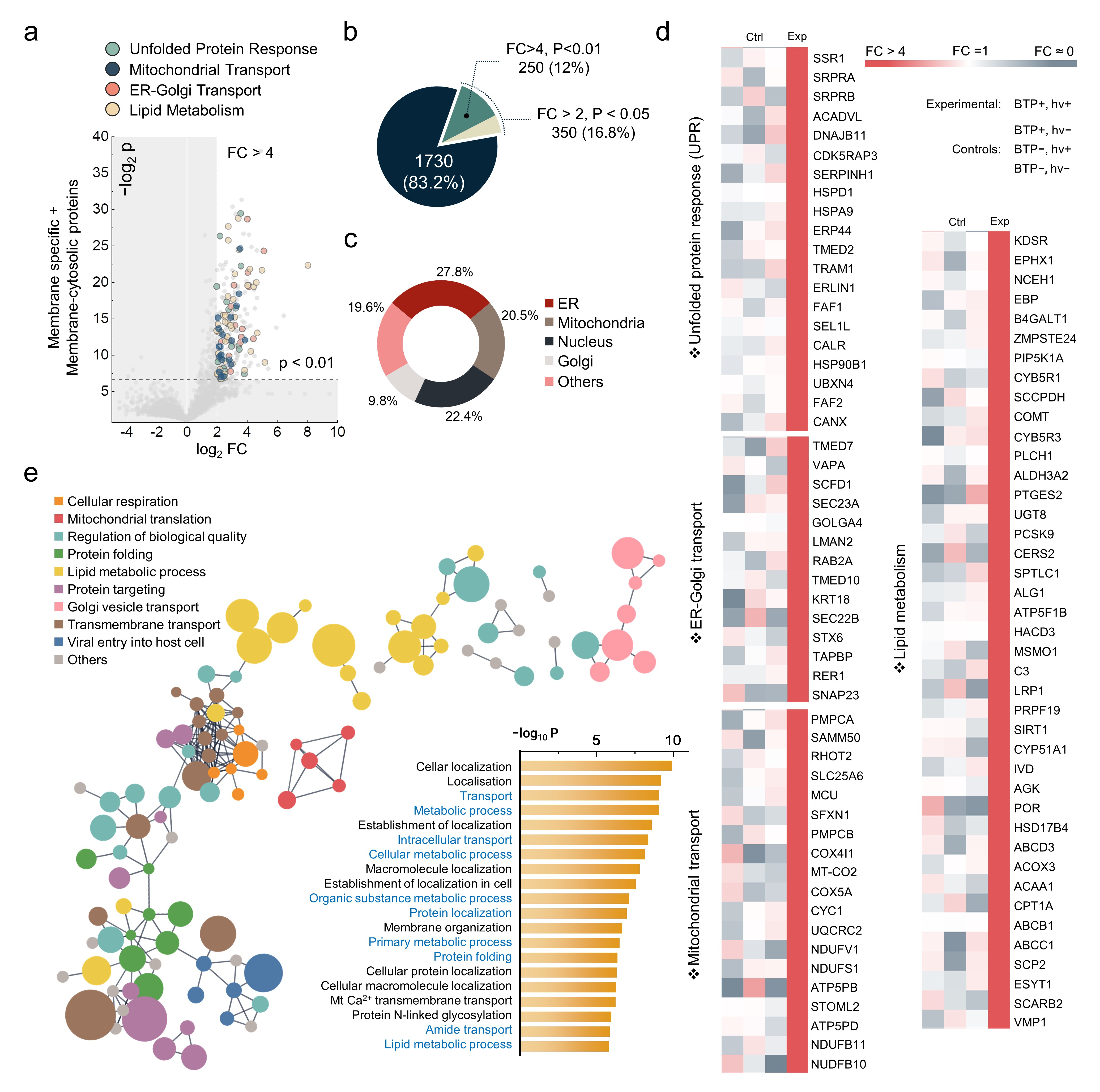
Figure 2. Functional implication of oxidised membrane proteins by BTP photocatalysis.
Lead author Chaiheon Lee emphasized the importance of this discovery in the field of cancer treatment, particularly in challenging hypoxic environments where traditional therapies often fall short. The outcomes of the study have opened up new avenues for solid cancer immunotherapy and the management of various immune-related disorders.
Co-author Mingyu Park highlighted the synergistic potential of this novel treatment approach with immunotherapy, particularly in overcoming the limitations of existing medications in hypoxic conditions.

Figure 3. Caspase-4/5-mediated pyroptosis by oxidative photocatalysis on membranes.
This study has garnered support from various organizations and has led to preclinical experiments conducted by UNIST-affiliated tech startup, O₂MEDI Inc. Encouraging results from these experiments, including successful tumor elimination in animal models of pancreatic cancer, have laid the groundwork for potential future applications in cancer therapy.
The findings of this research have been published in the online version of Nature Communications on May 13, 2024. It has been carried out through the support provided by O₂MEDI Inc., the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), TIPS, the National Cancer Centre (NCC), and UNIST.
Journal Reference
Chaiheon Lee, Mingyu Park, W. C. Bhashini Wijesinghe, et al,, "Oxidative photocatalysis on membranes triggers non-canonical pyroptosis," Nat. Commun., (2024).






