Solid-state batteries, currently used in small electronic devices like smart watches, have the potential to be safer and more powerful than lithium-ion batteries for things such as electric cars and storing energy from solar panels for later use. However, several technical challenges remain before solid-state batteries can become widespread.

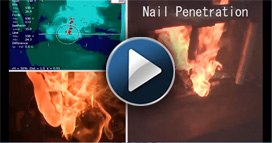
Alex Bates, front, and John Hewson, Sandia National Laboratories engineers, examine a lithium-ion battery in front of a specially designed battery testing chamber. They compared the heat released by a traditional lithium-ion battery to the heat released by a solid-state battery and a solid-state battery with a little liquid electrolyte. They found in many cases solid-state batteries with a little liquid electrolyte were safer than their lithium-ion counterparts. (Photo by Rebecca Gustaf) Click on the thumbnail for a high-resolution image.
A Sandia National Laboratories-led study, published on March 7 in the scientific journal Joule, tackled one of these challenges - a long-held assumption that adding some liquid electrolyte to improve performance would make solid-state batteries unsafe. Instead, the research team found that in many cases solid-state batteries with a little liquid electrolyte were safer than their lithium-ion counterparts. They also found, if the battery were to short-circuit, releasing all its stored energy, the theoretically super-safe, all-solid-state battery could put out a dangerous amount of heat.
"Solid-state batteries have the potential to be safer, and they have the potential for higher energy density," said Alex Bates, a Sandia postdoctoral researcher who led the study for the paper. "This means, for electric vehicles, you could go farther in between charges, or need fewer batteries for grid-scale energy storage. The addition of liquid electrolyte may help bridge the gap to commercialization, without sacrificing safety."
Better batteries through chemistry
Solid-state batteries are somewhat like lithium-ion batteries. In both, lithium ions move from one side of the battery to the other, while electrons flow through a circuit to power the device. One big difference is that throughout a lithium-ion battery, there is a substance that helps the lithium ions move quickly: the liquid electrolyte.
Loraine Torres-Castro, a battery safety expert in Sandia's Battery Abuse Testing Laboratory who is involved in the project, compares liquid electrolyte to a fleet of cars pulling into driveways: It shuttles lithium ions directly where they need to go. However, current liquid electrolytes are flammable and can cause a battery explosion or fire, especially when the battery is damaged.