Scientists at UCL and the Francis Crick Institute have studied how proteins accumulate in the wrong parts of brain cells in motor neurone disease, and have demonstrated how it might be possible, in some cases, to reverse this.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neurone disease, is a progressive fatal disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, causing loss of muscle control, with patients become increasingly paralysed and losing the ability to speak, eat and breathe.
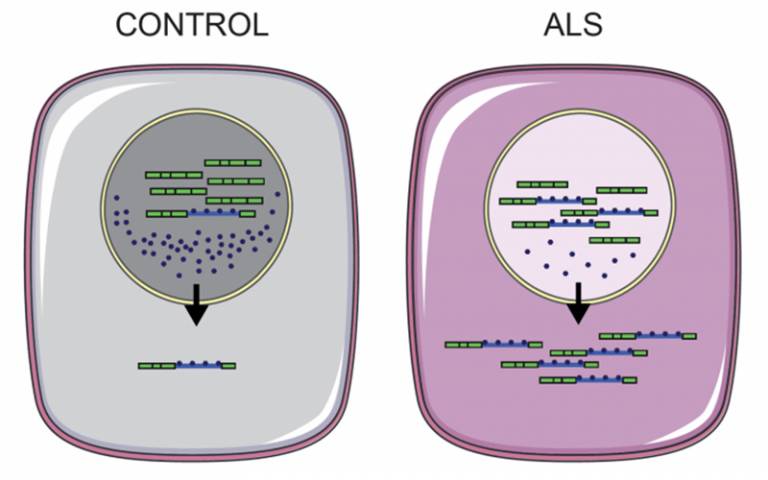
A common occurrence, in 97% of ALS cases, is the abnormal accumulation of proteins involved in the regulation of RNA, called RNA binding proteins, from a motor neuron's nucleus into the surrounding cytoplasm (the fluid that fills a cell).
In a new study, published in Brain Communications today, the researchers used motor neurons grown in the lab from skin cells donated by patients with ALS and showed it is possible to reverse the incorrect localisation of three RNA binding proteins. The patients who donated cells all had mutations in an enzyme called VCP. This mutation is only present in a small proportion of ALS cases.*
They found that the abnormal location of these proteins can be caused when the VCP enzyme is mutated, which has been shown to increase its activity.
Importantly, when the researchers blocked the activity of this enzyme in diseased cells, the distribution of proteins between the nucleus and the cytoplasm returned to normal levels. The inhibitor they used is similar to a drug which is currently being tested in phase II cancer trials and also blocks the activity of VCP.
First author Dr Jasmine Harley (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology and the Francis Crick Institute) said: "Demonstrating proof-of-concept for how a chemical can reverse one of the key hallmarks of ALS is incredibly exciting. We showed this worked on three key RNA binding proteins, which is important as it suggests it could work on other disease phenotypes too.
"More research is needed to investigate this further. We need to see if this might reverse other pathological hallmarks of ALS and also, in other ALS disease models."
Work to try and understand the disease mechanisms of ALS is ongoing, as seen in a second study the same group recently published in Brain. The scientists investigated intron-retaining transcripts, sections of RNA that are usually cut out of the genetic sequence during a process known as splicing, which also move from the cell nucleus to cytoplasm in ALS. By analysing RNA in diseased motor neurons, they identified over 100 types of intron-retaining transcripts in the cytoplasm.
Co-first author of the Brain paper, Dr Giulia Tyzack (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology and the Francis Crick Institute) said: "We were quite surprised about the number of different intron-retaining transcripts we found in cells with ALS, which exit the nucleus and enter the cytoplasm. We were not expecting to observe this to this degree."
Co-first author, PhD student Jacob Neeves (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology and the Francis Crick Institute), said: "To imagine what's going on here we can consider watching a movie at the cinema. Typically, we don't expect to see adverts throughout the film, but, if something goes wrong these ads might start cropping up at odd and unexpected points. These retained introns are a little bit like these abnormal ad breaks."
The scientists suggest that the collection of intron-retaining transcripts in the cytoplasm may be a factor which attracts RNA binding proteins to move into the cytoplasm, although more research is needed to confirm this.
Senior author of both papers, Professor Rickie Patani Tyzack (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, Francis Crick Institute and UCLH) said: "Together, our two papers show how laboratory science is furthering our understanding of such a complex and devastating disease and provides some reassurance that the development of effective treatments may be possible in the future."






