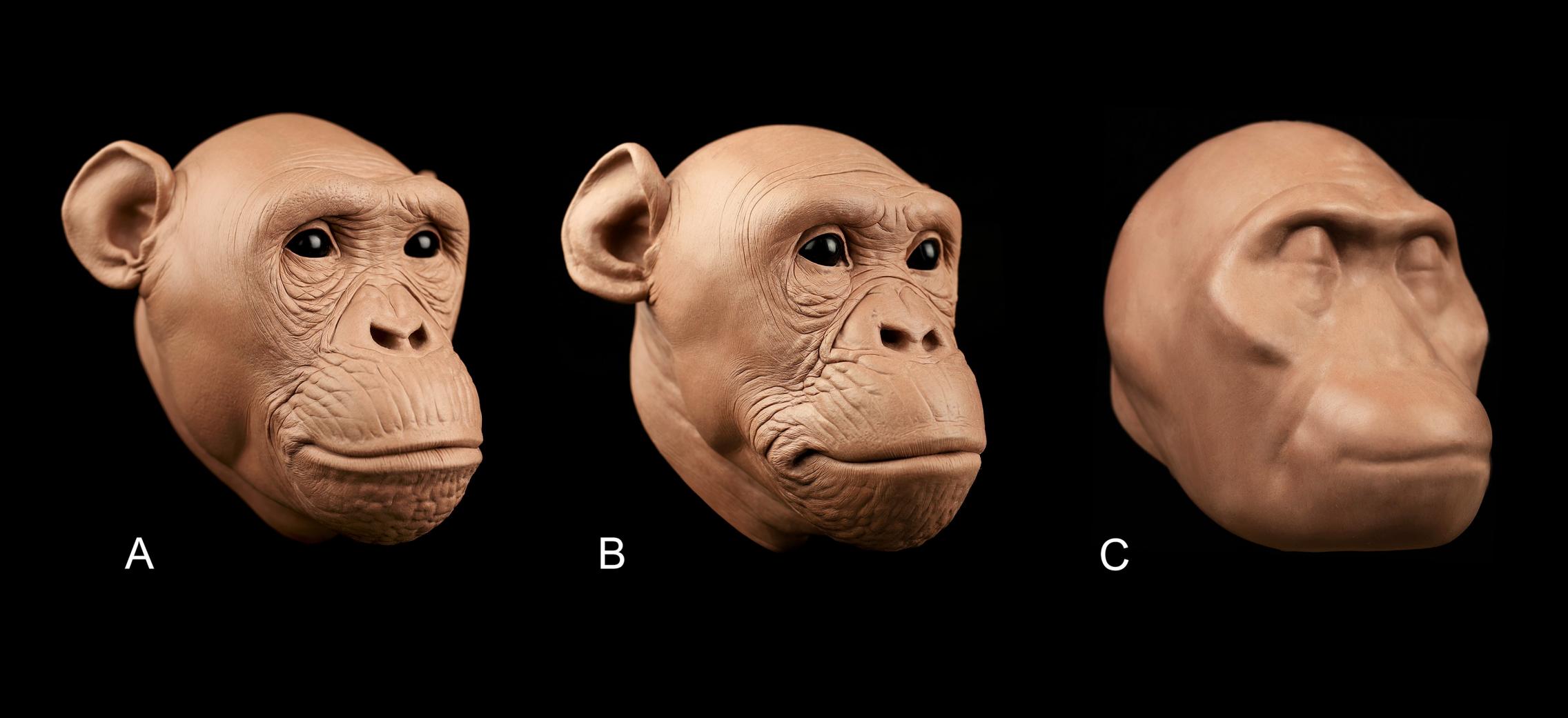
The soft tissue for these approximations of hominid faces was predicted using equations developed by the authors. No facial features are present in the ancient hominid (C), as the authors admit their equations say nothing about them. Image: Ryan M. Campbell.
Accurate soft tissue measurements are critical when making reconstructions of human ancestors, a new study from the University of Adelaide and Arizona State University has found.
"Reconstructing extinct members of the Hominidae, or hominids, including their facial soft tissue, has become increasingly popular with many approximations of their faces presented in museum exhibitions, popular science publications and at conference presentations worldwide," said lead author PhD student Ryan M. Campbell from the University of Adelaide.
"It is essential that accurate facial soft tissue thickness measurements are used when reconstructing the faces of hominids to reduce the variability exhibited in reconstructions of the same individuals."
Hominids have been readily accepted to line the halls of even the most trusted institutions. They are predominantly used for disseminating scientific information to the public in museum displays and students in university courses, which will influence the way humanity is perceived and defined more generally.
"Up until now soft tissue reconstruction has been based on mean tissue depth measurements which does not take into account variation in tissue depths between individuals," says Mr Campbell.
In this study, published in the journal PLOS One, the authors have formulated a facial soft tissue thickness dataset for adult chimpanzees, and a set of regression equations that can be used to reconstruct the soft tissues for ancient hominids, such as those dated from 4.0 to 1.2 million years ago.
"Up until now soft tissue reconstruction has been based on mean tissue depth measurements which does not take into account variation in tissue depths between individuals."Ryan M. Campbell






