Working in mice, the team identified the precise molecular targets of transplant rejection and showed how this knowledge could potentially be used in the future to improve immune monitoring of clinical transplant recipients.
The study is published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Each year around 1500 Australian lives are saved through organ transplants, but the risk of that transplant being rejected remains significant. Rejection occurs when a person's immune system recognises the organ as foreign and starts to attack it, just like it would a virus.
"While the early outcomes of organ transplants are excellent, the long-term results aren't nearly as good with many people losing their transplant within 10 to 15 years," said senior author Associate Professor Alexandra Sharland from the University of Sydney's Charles Perkins Centre and Faculty of Medicine and Health.
Clinicians currently detect transplant rejection through a range of techniques, including monitoring organ function via blood tests or more invasive procedures such as regular biopsies of the transplanted organ.
However, once evidence of damage is apparent it may not be completely reversible, eventually leading to transplant loss.
Associate Professor Helen Pilmore, President of the Transplantation Society of Australia and New Zealand said: "The findings of the pre-clinical study in mice could, if transferable to humans, have significant implications for clinical transplant management."
"We hope that one day this research could lead to a simple blood test that is able to distinguish the donor reactive T cells-that is the cells that can specifically recognise the transplanted organ as foreign and respond to it, from all the other cells," said co-author Dr Nicole Mifsud, Group Leader of the Clinical Immunology Laboratory at the Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute.
"This could potentially be used to identify which patients are at risk of rejection or to accurately adjust the level of immunosuppression, the drugs used to lower the body's ability to reject the organ. Using the appropriate level of immunosuppressants can prove vital to maintaining the viability of transplanted organs."
The study explained
In this study, the researchers were able to definitively answer an ongoing question in transplant research - whether self-peptides (short fragments of proteins produced inside cells) in association with foreign MHC molecules (a molecule on the outside of cells which differs between donor and recipient) are recognised by the bulk of donor-reactive T cells - in turn causing transplant rejection.
After confirming this, the team then constructed a laboratory procedure to accurately identify and quantify the majority of donor-reactive T cells in a rejecting skin graft.
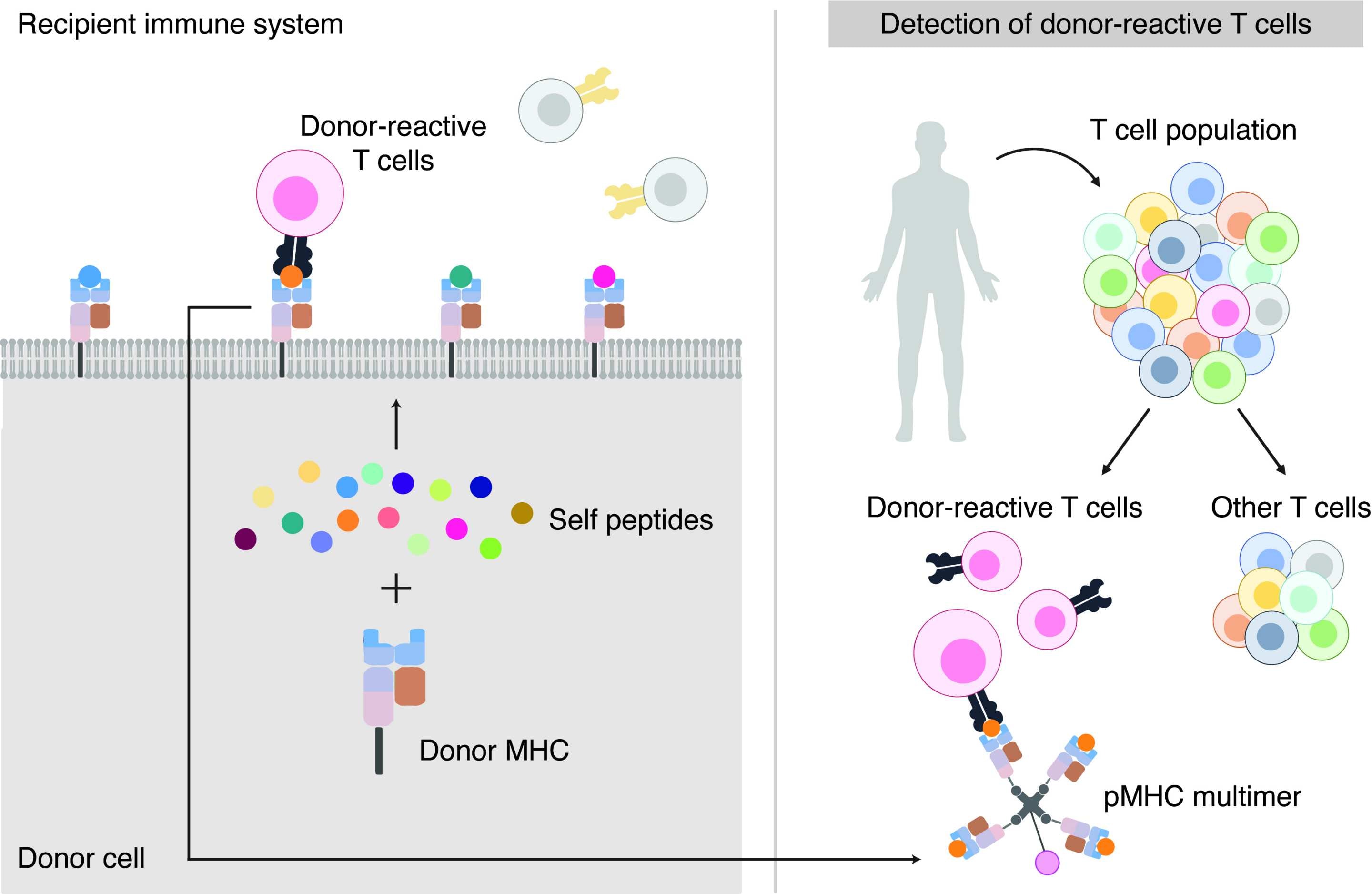
Figure 1: The research team discovered that self-peptides pairing with foreign MHC molecules are recognised by donor-reactive T cells, leading to transplant rejection.
Figure 2: If the same applies in humans this discovery could be used as the basis of a diagnostic test to accurately distinguish the presence of donor reactive T cells from all other T cells present.
The researchers' next step will be to analyse the molecules in humans (which are different to those in mice) using the same scientific approach.
The study was made possible by a research collaboration that brought together the University of Sydney's strength in transplant immunobiology with Monash University's leading expertise in immunopeptidomics. Co-author Professor Anthony Purcell from Monash University said the published findings are the fruit of nearly 10 years of teamwork by the research groups.
A transplant recipient's experience
When a newlywed in 2006, Wendy Jenkins was diagnosed with a life-threatening lung condition and given only two years to live. She was lucky enough to be matched with an organ donor and it is now 14 years since her transplant.
"I am however very mindful that chronic organ rejection is one of the key factors in limiting long-term survival for lung transplant patients such as myself, with the average life expectancy post lung transplant in Australia being only seven years. It would be an exciting prospect if doctors could better manage this risk by having a simple blood test to monitor the exact immune cells that cause this rejection," said Ms Jenkins.
Declaration: This study was funded by the NHMRC (Ideas grant APP1183806 and Principal Research Fellowship 1137739) and the Myee Codrington Medical Research Foundation. Alexandra Sharland, Nicole Mifsud, Anthony Purcell and their colleagues are inventors on patent PCT/AU2020/051221, held by Monash University and the University of Sydney.






