A new study published in Advanced Science has revealed how curcumin, a bioactive compound found in Curcuma aromatica (Yujin), can help mitigate neuroinflammation and brain damage caused by epileptic seizures.
The study, led by MENG Wenxiang's team from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with XIE Qi's team from the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, provides valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms through which curcumin regulates the brain's inflammatory response, opening up new avenues for the treatment of epilepsy.
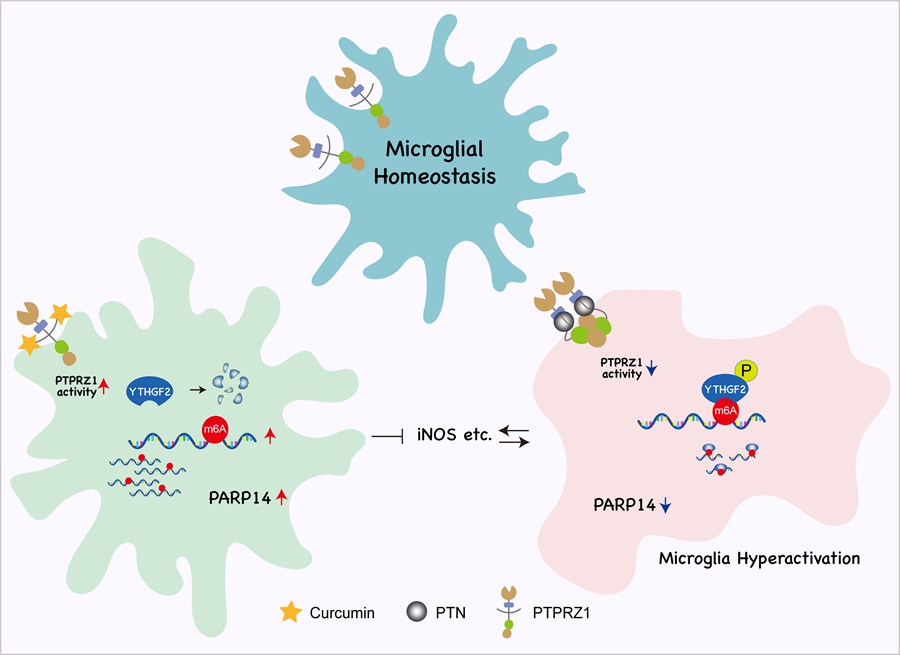
Epilepsy, a severe neurological disorder, is characterized by recurrent seizures that not only cause neuronal damage but also activate glial cells, triggering a local immune response. This immune response releases pro-inflammatory factors that contribute to a vicious cycle that worsens the condition. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has long employed Baijin Pills, which contain curcumin, for epilepsy treatment. However, the exact molecular mechanisms by which curcumin modulates neuroinflammation have remained largely unclear until now.
The researchers found that curcumin regulates the protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type Z1 (PTPRZ1), suppressing excessive neuroinflammatory responses, reducing brain damage following seizures, and promoting neuronal repair. These findings enhance our understanding of curcumin's pharmacological effects and identify new therapeutic targets and strategies for treating neurological disorders.
The discovery of effective formulations, the elucidation of scientific mechanisms, and the expansion of clinical applications are the core goals of modern TCM research. Curcumin is widely found in Curcuma aromatica (Yujin), Curcuma longa (Jianghuang), and Curcuma phaeocaulis (E Zhu) - traditional medicinal herbs that have been used for centuries in China and other Asian countries to treat various ailments. The biological activity and pharmacological effects of curcumin have attracted much attention.
This study advances the understanding of curcumin's role in regulating the neuroinflammation and lays the foundation for further research into its therapeutic potential in treating neurological diseases. It also emphasizes the importance of modern TCM research in elucidating the mechanisms behind traditional remedies and their clinical applications.
The study was funded by the Major Research Projects of the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences Innovation Program and the Beijing Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Development Fund.