
Ukraine has not been invited to a key meeting between American and Russian officials in Saudi Arabia this week to decide what peace in the country might look like.
Author
- Matt Fitzpatrick
Professor in International History, Flinders University
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky said Ukraine will " never accept " any decisions in talks without its participation to end Russia's three-year war in the country.
A decision to negotiate the sovereignty of Ukrainians without them - as well as US President Donald Trump's blatantly extortionate attempt to claim half of Ukraine's rare mineral wealth as the price for ongoing US support - reveals a lot about how Trump sees Ukraine and Europe.
But this is not the first time large powers have colluded to negotiate new borders or spheres of influence without the input of the people who live there.
Such high-handed power politics rarely ends well for those affected, as these seven historical examples show.
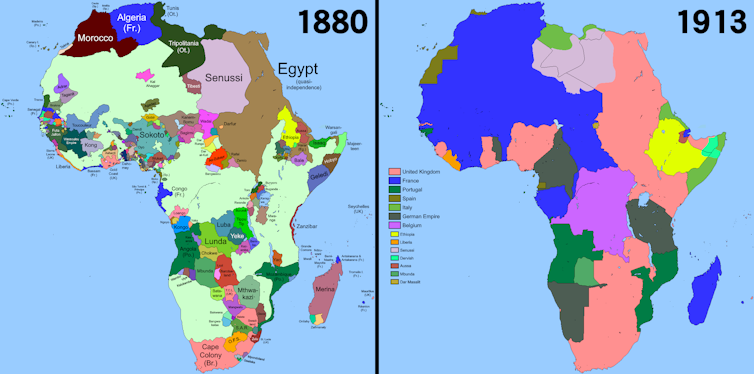
1. The Scramble for Africa
In the winter of 1884-85, German leader Otto von Bismarck invited the powers of Europe to Berlin for a conference to formalise the division of the entire African continent among them. Not a single African was present at the conference that would come to be known as " The Scramble for Africa ".
Among other things, the conference led to the creation of the Congo Free State under Belgian control, the site of colonial atrocities that killed millions.
Germany also established the colony of German South West Africa (present-day Namibia), where the first genocide of the 20th century was later perpetrated against its colonised peoples.
2. The Tripartite Convention
It wasn't just Africa that was divided up this way. In 1899, Germany and the United States held a conference and forced an agreement on the Samoans to split their islands between the two powers.
This was despite the Samoans expressing a desire for either self-rule or a confederation of Pacific states with Hawai'i.
As "compensation" for missing out in Samoa, Britain received uncontested primacy over Tonga.
German Samoa came under the rule of New Zealand after the first world war and remained a territory until 1962. American Samoa (in addition to several other Pacific islands) remain US territories to this day.
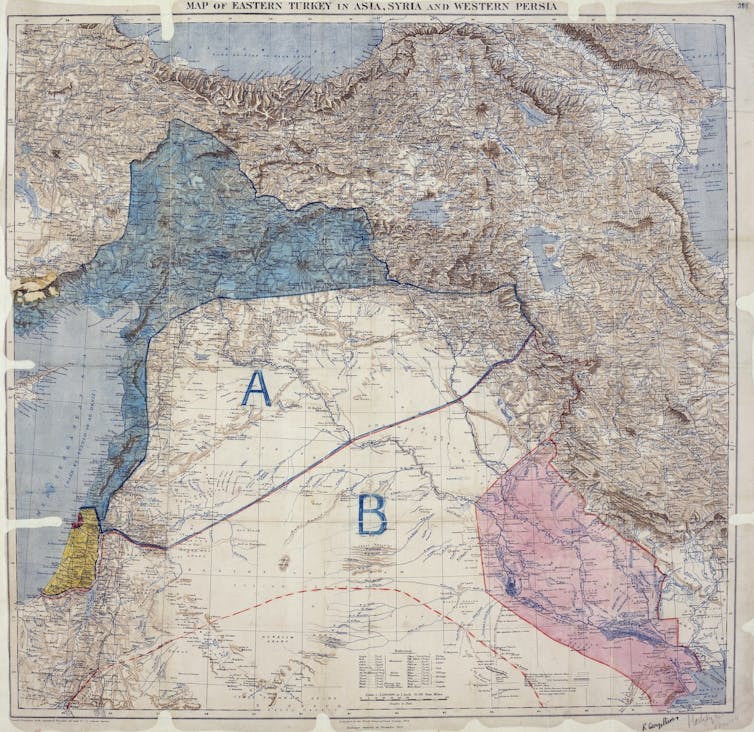
3. The Sykes-Picot Agreement
As the first world war was well under way, British and French representatives sat down to agree how they'd divide up the Ottoman Empire after it was over. As an enemy power, the Ottomans were not invited to the talks.
Together, England's Mark Sykes and France's François Georges-Picot redrew the Middle East's borders in line with their nations' interests.
The Sykes-Picot Agreement ran counter to commitments made in a series of letters known as the Hussein-McMahon correspondence . In these letters, Britain promised to support Arab independence from Turkish rule.
The Sykes-Picot Agreement also ran counter to promises Britain made in the Balfour Declaration to back Zionists who wanted to build a new Jewish homeland in Ottoman Palestine.
The agreement became the wellspring of decades of conflict and colonial misrule in the Middle East, the consequences of which continue to be felt today.
4. The Munich Agreement
In September 1938, British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain and French Prime Minister Édouard Daladier met with Italy's fascist dictator, Benito Mussolini, and Germany's Adolf Hitler to sign what became known as the Munich Agreement .
The leaders sought to prevent the spread of war throughout Europe after Hitler's Nazis had fomented an uprising and began attacking the German-speaking areas of Czechoslovakia known as the Sudetenland. They did this under the pretext of protecting German minorities. No Czechoslovakians were invited to the meeting.
The meeting is still seen by many as the "Munich Betrayal" - a classic example of a failed appeasement of a belligerent power in the false hope of staving off war.
5. The Évian Conference
In 1938, 32 countries met in Évian-les-Bains, France, to decide how to deal with Jewish refugees fleeing persecution in Nazi Germany.
Before the conference started, Britain and the US had agreed not to put pressure on one another to lift the quota of Jews they would accept in either the US or British Palestine.
While Golda Meir (the future Israeli leader) attended the conference as an observer, neither she nor any other representatives of the Jewish people were permitted to take part in the negotiations.
The attendees largely failed to come to an agreement on accepting Jewish refugees, with the exception of the Dominican Republic. And most Jews in Germany were unable to leave before Nazism reached its genocidal nadir in the Holocaust.
6. The Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
As Hitler planned his invasion of Eastern Europe, it became clear his major stumbling block was the Soviet Union. His answer was to sign a disingenuous non-aggression treaty with the USSR.

The treaty, named after Vyacheslav Molotov and Joachim von Ribbentrop (the Soviet and German foreign ministers), ensured the Soviet Union would not respond when Hitler invaded Poland. It also carved up Europe into Nazi and Soviet spheres. This allowed the Soviets to expand into Romania and the Baltic states, attack Finland and take its own share of Polish territory.
Unsurprisingly, some in Eastern Europe view the current US-Russia talks over Ukraine's future as a revival of this kind of secret diplomacy that divided the smaller nations of Europe between large powers in the second world war.
7. The Yalta Conference
With the defeat of Nazi Germany imminent, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, Soviet dictator Josef Stalin and US President Franklin D Roosevelt met in 1945 to decide the fate of postwar Europe. This meeting came to be known as the Yalta Conference .
Alongside the Potsdam Conference several months later, Yalta created the political architecture that would lead to the Cold War division of Europe.
At Yalta, the "big three" decided on the division of Germany, while Stalin was also offered a sphere of interest in Eastern Europe.
This took the form of a series of politically controlled buffer states in Eastern Europe, a model some believe Putin is aiming to emulate today in eastern and southeastern Europe.
![]()
Matt Fitzpatrick receives funding from the Australian Research Council. He is affiliated with the History Council of South Australia.






